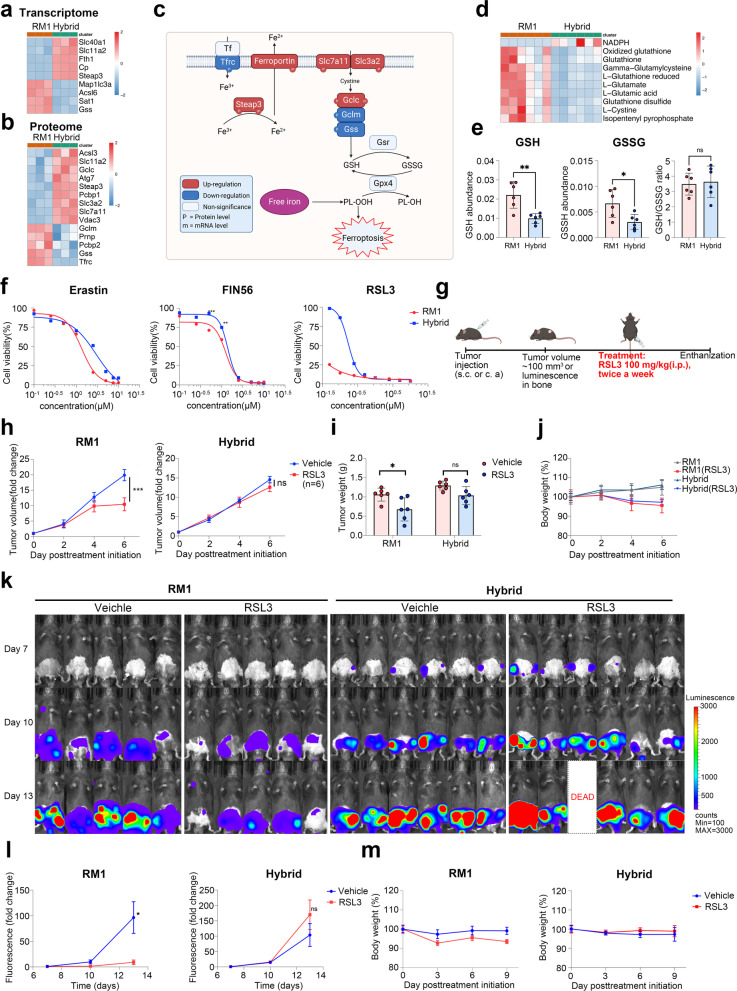
Fig. 8.
Tumor hybrid cells are resistant to ferroptosis in vitro and in vivo. a, b Heatmap showing the differentially expressed genes (a) or proteins (b) in the ferroptosis pathway between RM1 cells and hybrid tumor cells. c Diagram showing the changes in key genes involved in ferroptosis. d Heatmap showing the differential metabolites related to ferroptosis between RM1 cells and hybrid cells. e The level of GSH, GSSH, and GSH/GSSH in RM1 cells and hybrid cells. f Viability of RM1 cells and hybrid cells after erastin, FIN56, or RSL3 treatment. g Schematic illustration of the experimental design using RSL3 treatment. h The growth curve of RM1 tumor or hybrid tumors after treatment with RSL3 (n = 6). i Tumor weight measured at the endpoint of the experiment after treatment with erastin (n = 6). j The growth curve of body weight in mice treated with RSL3 or vehicle (n = 6). k, l Representative bioluminescence images (k) and growth kinetics (l) of bioluminescence in mice after inoculation with RM1 (n = 5) or hybrid cells (n = 6) through the caudal artery. m The growth curve of body weight in mice treated with RSL3 or vehicle (n = 5 or 6). ns: not significant, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001