Figure 7.
Model for signal-anchor topogenesis
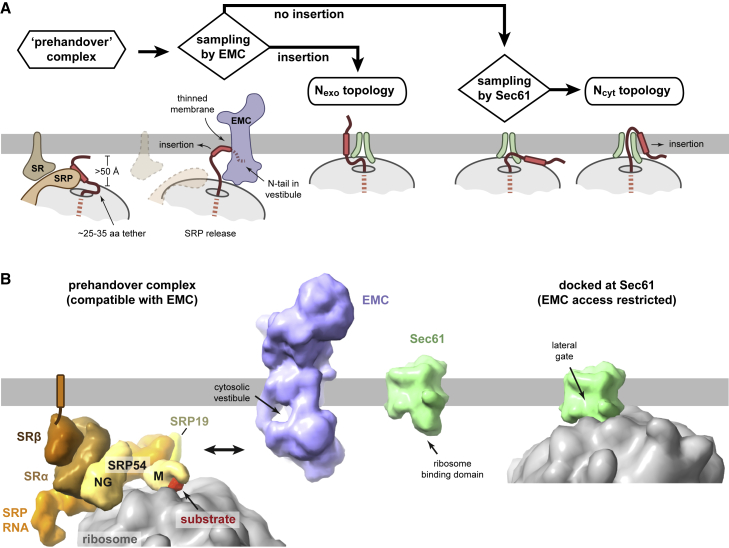
(A) After targeting, the SRP-SR complex rearranges into the prehandover configuration. The large size of the SRP-SR complex precludes the ribosome exit tunnel from approaching the membrane (see B), thereby allowing access to EMC without competition from Sec61. Release of the SA from SRP allows SA binding to the membrane and sampling of EMC’s cytosolic vestibule by the N-tail. The SA can reach the membrane because a downstream tether of more than 25 aa has already been synthesized by this point. The EMC sampling step is transient and once the SRP-SR complex dissociates, the ribosome docks at Sec61, at which point access to EMC is restricted due to steric hinderance by the ribosome. If the SA was inserted during the EMC sampling step, the substrate achieves the Nexo topology. Otherwise, Sec61 can insert the SA in the Ncyt topology.
(B) Scale models illustrating that the large cytosolic domain of EMC can fit between the membrane and ribosome in the prehandover complex (left). By contrast, Sec61’s ribosome-binding domain cannot reach its site on the ribosome. After ribosome docking on Sec61 (right), EMC can no longer approach close to the exit tunnel. The prehandover complex is from PDB: 6FRK.49 EMC is from a composite of PDB: 7ADO,46 PDB: 6Z3W,28 and AlphaFold2.50 The ribosome-Sec61 complex is from PDB: 3J7R.51