Fig. 2.
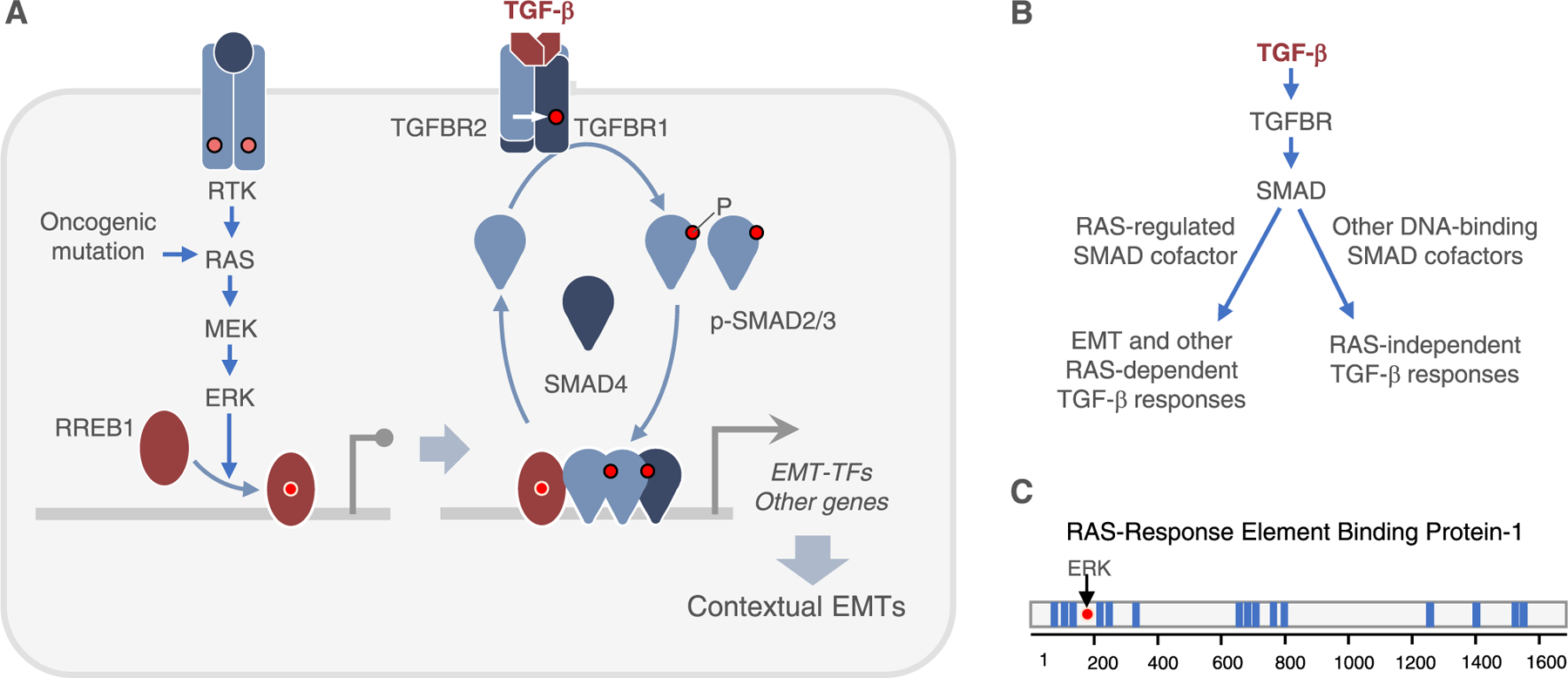
TGF-β and RAS collaboration in the induction of EMTs. A. RAS-MAPK signaling is an determines a cell’s competence to undergo EMT in response to TGF-β. RAS activation by receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) or oncogenic mutation leads the ERK phosphorylation of RREB1, enabling its binding to cognate sites genome-wide. RREB1 binds near SMAD binding sites. TGF-β receptors activate SMAD transcription factors for activation of EMT-TFs and other genes in collaboration with RREB1, triggering different types of EMTs in different contexts. B. Only a subset of TGF-β-SMAD target genes depend on RAS-MAPK input for activation. RREB1 collaborated with SMADs in the activation of these RAS-dependent genes. C. RREB1 contains 15 zinc-finger domains (blue bars) distributed in three clusters. ERK phosphorylation of a canonical MAPK site in the N-terminal domain of RREB1 stimulates binding to DNA.
