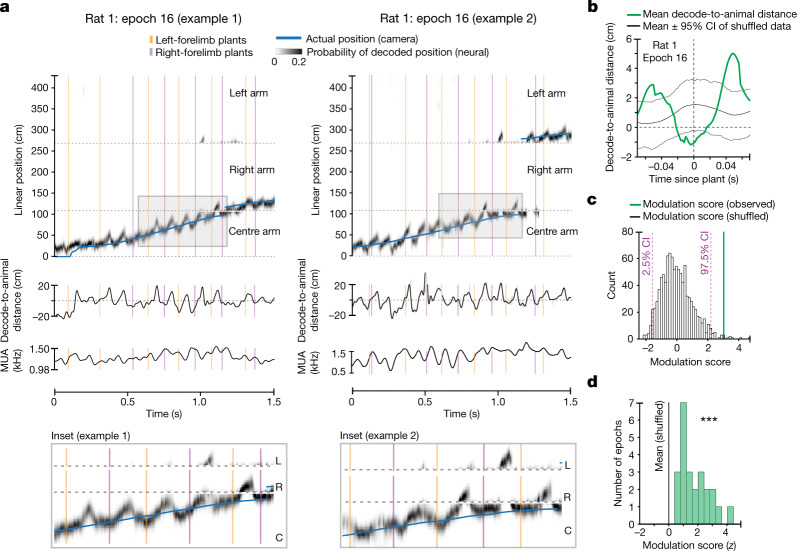
Fig. 2. Synchronization between hippocampal spatial representations and forelimb plant times.
a, Estimation of the represented position on the basis of clusterless decoding during outbound runs on the centre arm of the w-track. Blue trace represents the linearized position of the rat’s nose. Grey density represents the decoded position of the rat on the basis of spiking. Note that the decoded position can be ahead of, near or behind the rat’s current position. Orange and purple vertical lines represent the plant times of the left and the right forelimb, respectively. Shaded box indicates inset enlarged below. C, centre; R, right; L, left. b, Mean decode-to-animal distance trace triggered by forelimb plant times that precede non-local representations greater than 10 cm ahead of the rat’s current position for the selected region (60–100 cm) (green line; data from rat 1, epoch 16). Grey lines represent the 95% confidence interval (CI) of the shuffled distribution. The dotted line at zero indicates decode-to-animal distance values corresponding to the actual position of the rat’s nose, and positive or negative values indicate represented positions ahead or behind the actual position of the rat, respectively. c, Decode-to-animal distance modulation score of the observed data (vertical line, green) and the histogram of the modulation score for the shuffled distributions (bars, grey). d, Distribution of the decode-to-animal distance modulation score for the observed data in all rats (green bars) versus the mean of the modulation score for the shuffled data (black vertical line; n = 24 epochs in 4 rats, two-sided t-test: P = 1.6 × 10−8; individual animal P values: P (rat 1), 4 × 10−3; P (rat 2), 5 × 10−3; P (rat 3), 4 × 10−4; P (rat 5), 0.04; Benjamini–Hochberg adjusted P values: P (rat 1), 7 × 10−3; P (rat 2), 7 × 10−3; P (rat 3), 2 × 10−3; P (rat 5), 0.04). P < 0.0005.