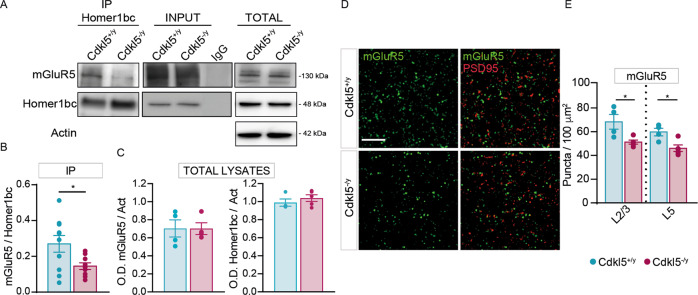
Fig. 1. CDKL5 loss is responsible for both the disruption of mGluR5-Homer1bc interaction and the reduction of mGluR5 localization in the cortical neuropil.
A Co-IP of cortical synaptosomal fraction (P2) from P56 mice by using anti-Homer1bc. IgG: control lane in the absence of antibodies. Immunoprecipitates, inputs (P2) and total cortical lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for mGluR5 and Homer1bc. B, C Bar graphs showing Co-IP (B) and total cortical lysates (C) quantitation expressed as optical density (O.D.). D Confocal microscopy images showing mGluR5+ (green) and PSD-95+ (red) immunopuncta in layers II/III of S1 cortex (scale bar: 5 µm). E Bar graphs displaying the density of mGluR5+ puncta. Student T test *p < 0.05 (Co-IP: n = 8; WB: n = 4 IFL: n = 4).