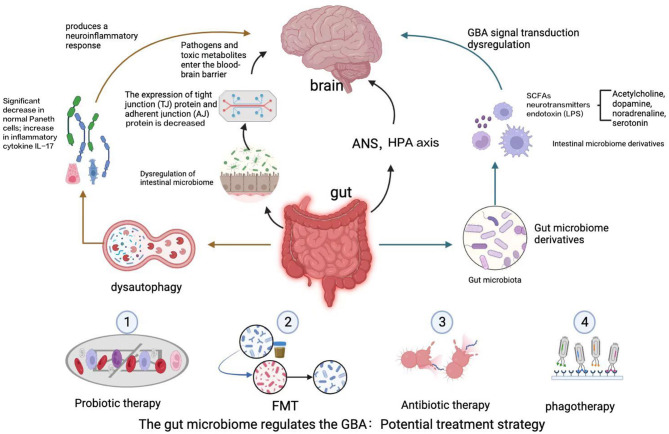
Figure 1.
The GBA is a bidirectional communication pathway between the gut and the CNS involving multiple feedback loops. Changes in the gut microbiota lead to alterations in the intestinal epithelial barrier, and the gut microbiota produces a variety of neuroactive metabolites, including SCFAs, neurotransmitters, and endotoxins. These factors affect autophagy, activate an immune response, and lead to dysregulation of the GBA via the ascending pathway from the gut to the brain, triggering neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system, such as ALS, AD, and PD. A potential avenue for treatment of ALS may involve manipulation of the gut microbiota and its derivatives, including via intestinal mucosal resurfacing, dietary intervention, probiotic supplementation, antibiotics, and post-antibiotic therapy, among other potential methods.