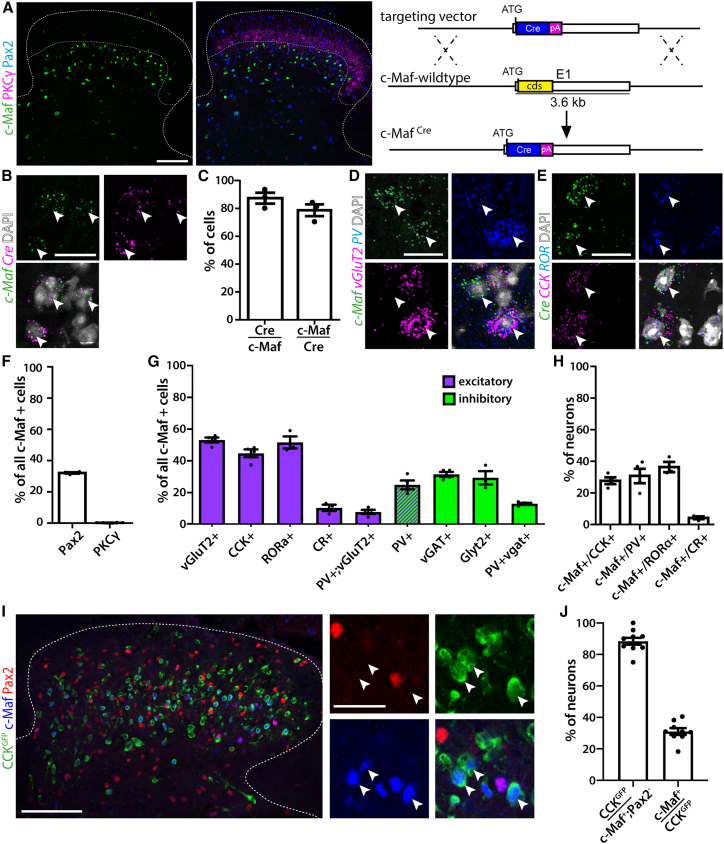
Figure 1.
c-Maf is expressed in subsets of deep dorsal horn interneurons
(A) c-Maf expression in the dorsal spinal cord and schematic representation of the generation of the c-MafCre allele.
(B) Double in situ hybridization showing the overlap between c-Maf and Cre mRNAs in the c-MafCre mouse spinal cord.
(C) Quantification of (B) (n = 3, 605 neurons).
(D) Triple in situ hybridization showing overlap between c-Maf-, VGlut2-, and PV-expressing neurons.
(E) Triple in situ hybridization showing overlap between Cre+ (c-Maf)-, CCK-, and RORα-expressing neurons.
(F) Quantification of the co-expression of c-Maf, Pax2, and PKCγ proteins as depicted in (A) (n = 4, 1,293 c-Maf+ neurons).
(G) Quantification of the proportion of c-Maf neurons expressing other markers of deep dorsal horn neurons (VGlut2: n = 4, 1,045 c-Maf+ neurons; CCK: n = 4, 848 c-Maf+ neurons; RORα: n = 3, 317 c-Maf+ neurons; CR: n = 3, 302 c-Maf+ neurons; PV: n = 4, 878 c-Maf+ neurons; vGAT: n = 4, 878 c-Maf+ neurons; Glyt2: n = 3, 302 c-Maf+ neurons). Magenta bars represent genes exclusively/predominantly expressed in excitatory neurons, while green bars represent co-expression with inhibitory marker genes.
(H) Quantification of the proportion of CCK+, PV+RORα+, and CR+ neurons expressing c-Maf (n = 4, 1,362 CCK+ and 513 PV+ neurons; n = 3, 734 CR+ and 454 RORα+ neurons).
(I) Co-labeling of GFP, Pax2, and c-Maf in the dorsal spinal cord of CCKGFP (CCKCre;ROSA26fls-NuTRAP) animals. Arrows indicate excitatory c-Maf neurons (c-Maf+;Pax2−) co-expressing GFP.
(J) Quantification of (I) (n = 3, 309 neurons). Note that the vast majority of excitatory c-Maf neurons (c-Maf+;Pax2−) co-express GFP while only one-third of the CCKGFP neurons co-express c-Maf.
Error bars denote ±SEM. Scale bars, 100 μm (A and I) and 20 μm (B, D, and E).