Figure 3.
Retrograde rabies virus-based tracing of monosynaptic input to c-Maf neurons
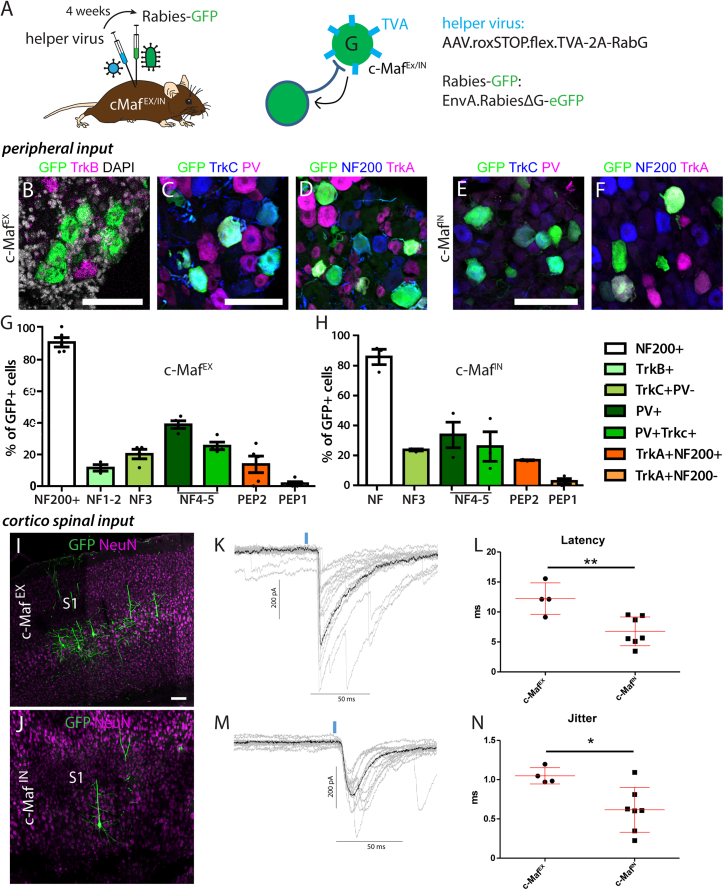
(A) A helper virus (TVA, RabG) was injected into the spinal cord of c-MafEX or c-MafIN mice, followed by injection of the EnvA-pseudotyped rabies virus (EnvA.RV.ΔG.eGFP).
(B–F) RNAscope labeling or immunofluorescence staining on DRG sections showing overlap between GFP and markers of retrogradely traced sensory neurons in c-MafEX (B–D) or c-MafIN (E and F) mice.
(G) Quantification of the number of GFP+ DRG neurons positive for NF200, TrkA (n = 5, 574 cells), PV and TrkC (n = 4, 349 cells), and TrkB (n = 3, 374 cells), in c-MafEX mice.
(H) Quantification of the number of GFP+ DRG neurons positive for NF200, TrkA (n = 3, 239 cells), PV, and TrkC (n = 3, 167 cells) in c-MafIN mice. In (G) and (H), NF1–5 and PEP1–2 refer to the classification of sensory neurons proposed by Usoskin et al.:35 NF = NF200+, NF1–2 = TrkB+, NF3 = TrkC+;PV−, NF4–5 = PV+;(TrkC low), PEP2 = TrkA+;NF200+, PEP1 = TrkA+, NF200−.
(I–N) (I and J) Immunofluorescence staining showing eGFP-labeled neurons in supraspinal sites retrogradely traced from c-MafEX (I–K) or c-MafIN (L–N) neurons. Neurons were found in the primary somatosensory cortex (CST neurons in layer 5 of S1, n = 4). (K–N) Slice recordings after optogenetic stimulation of ChR2-YFP expressing CST terminals in spinal cord slices (c-MafEX = 5 cells, c-MafIN = 7 cells). (K and M) Example traces recorded after optogenetic stimulation in c-MafEX or c-MafIN neurons. (L and N) Quantification of latencies and jitter recorded in c-MafEX or c-MafIN neurons.
Error bars denote ±SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 (unpaired Student’s t test). Scale bars, 100 μm.