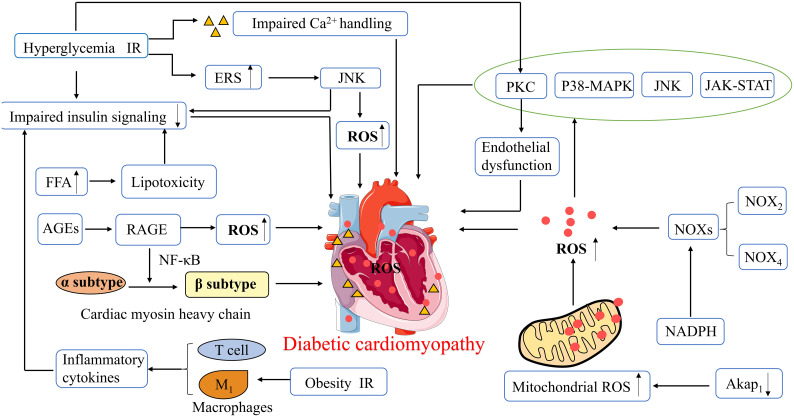
Figure 2.
Pathophysiological mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy. ROS, Reactive oxygen species; ERS, Endoplasmic reticulum stress; PKC, protein kinase C; p38 MAPK, p38 Mitogen activated protein kinase; JNK, Jun kinase; JAK -STAT, Janus kinase and signal transducer and activator of transcription; NADPH, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NOXs, NADPH Oxidases; Akap1, A-kinase anchoring protein 1; FFA, Free fatty acids; AGEs, Advanced glycation end-products; RAGE, AGE receptor; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; IR, Insulin resistance.