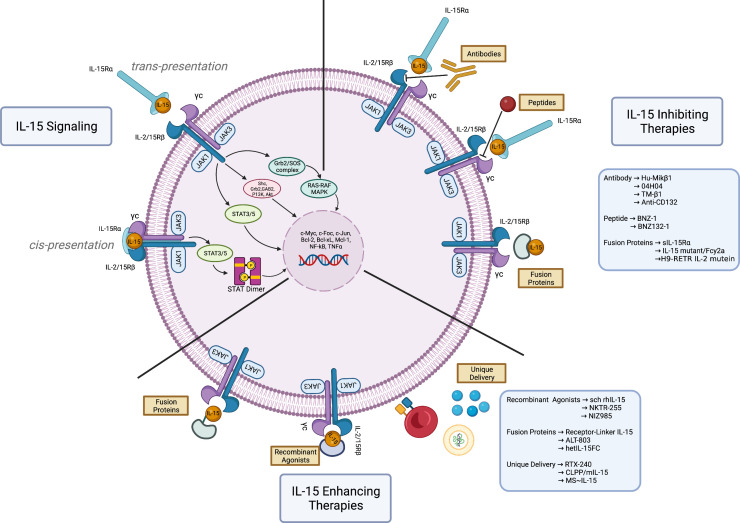
Figure 1.
Therapeutic approaches on Interleukin-15 signaling. IL-15 signaling. Interleukin-15 (IL-15) plays a major role in the immune responses by serving as a growth factor for T- and NK-cells. Normal IL-15 signaling begins following the binding of IL-15, produced by dendritic cells, with its high affinity receptor IL-15Rα on the same cells (cis presentation). Upon binding, it is trans-presented to the IL-2R/15Rβ-γc receptor complex expressed by T- and NK-cells, which consequently activates JAK1/JAK3 along with STAT3/5, PI3K/Akt and Ras/Raf/MAPK. These signaling cascades trigger a transcriptional program aimed at boosting the anti-pathogens inflammatory response and enhancing the anti-tumoral immune response. Paradoxically, the overexpression of IL-15 can result in the development of hematological malignancies. IL-15 inhibiting therapies. Numerous interventions have been developed to block IL-15 signaling and the T- and NK-cells tumoral proliferation. Some examples are anti-IL-15 antibody (Hu-Mikβ1, 04H04, TM-β1, anti-CD-132), peptide antagonists (BNZ-1, BNZ132-1), and fusion proteins (soluble IL-15Rα-sIL15Rα, IL-15 mutant/Fcγ2a, H9-RETR IL-2 mutein). IL-15 enhancing therapies. Highly efficient immune response enhancing agents have been developed to leverage the ability of IL-15 to boost the anti-tumoral effector cells. The figure depicts recombinant agonists (sch rhIL-15, NKTR-255, NIZ985), fusion proteins (receptor linker IL-15 or RLI, ALT-803, hetIL-15FC), and unique delivery systems (RTX-240, CLPP/mIL-15, MS~IL-15). These compounds boost the immune response against tumoral cells and can potentiate the effect of immunotherapy and adoptive cell therapy. Figure made with Biorender.com.