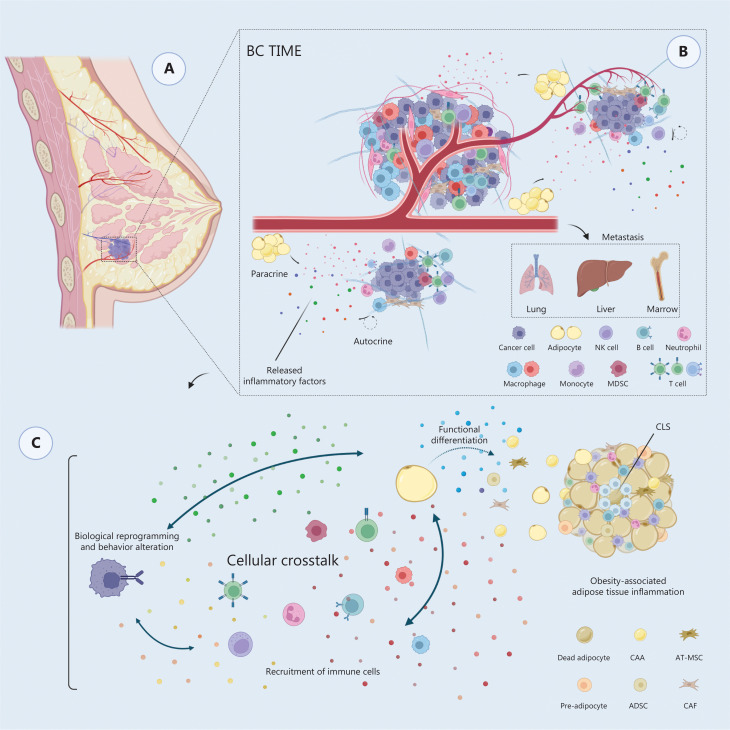
Figure 1.
Components and interactions of the BC TME containing adipocytes. (A) The mammary gland is mainly composed of acini and lobules. In the breast, epithelial cells infiltrate around adipose tissue, a unique cell group that maintains the breast morphology. (B) Composition of the TME, including both the physical and biochemical components in the stroma. (C) Schematic representation of interactions between the obesity-associated inflammatory microenvironment and the BC TME. Cellular crosstalk between cancer cells and stromal cell populations leads to various pathologic hallmarks of BC. TIME, tumor immune microenvironment; NK cell, natural killer cell; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; CLS, crown-like structure; CAA, cancer-associated adipocyte; AT-MSC, adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell; ADSC, adipose-derived stem cell; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast.