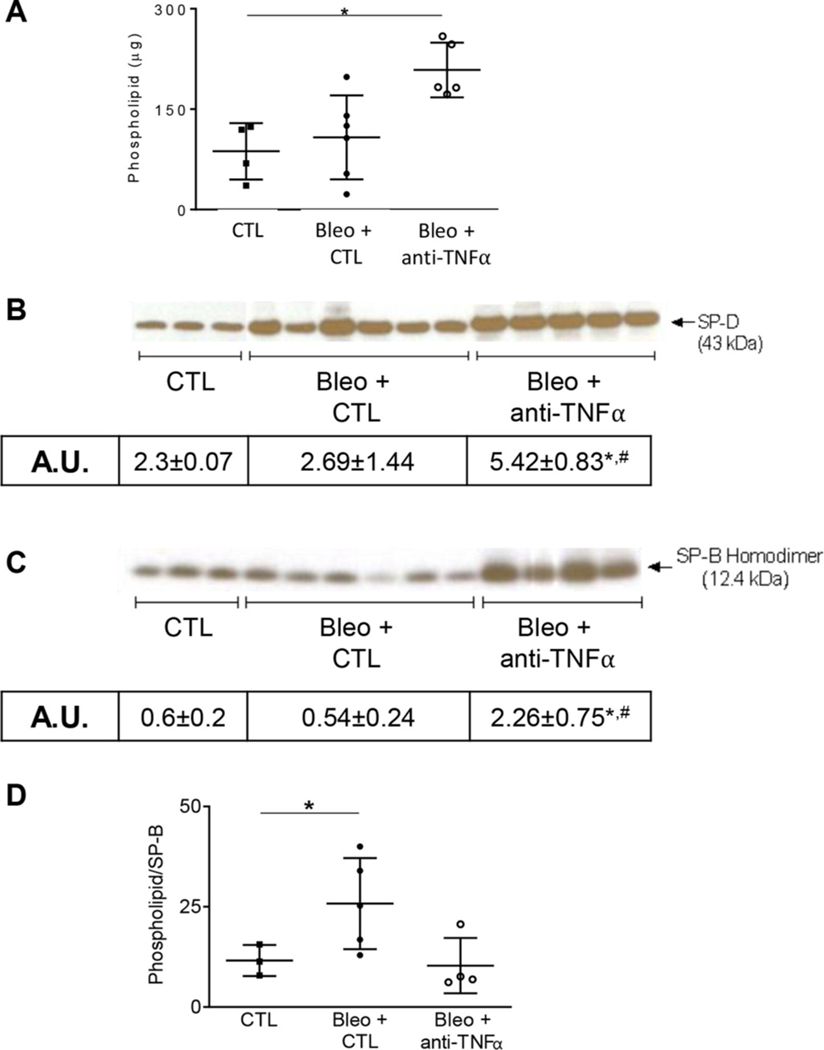
Fig. 6.
Effects of anti-TNFα administration on bleomycin-induced alterations in surfactant protein expression. Panels A-C: Whole BAL and large aggregate fractions, collected at 0 d (CTL) and 21 d after exposure to Bleo + CTL or Bleo + anti-TNFα, were assessed for total phospholipid content (Panel A), SP-D (Panel B) and SP-B (Panel C) by western blot analysis, respectively. Panel D: Total Phospholipid-to-SP-B ratio at 0 d (CTL) and 21 d after exposure to Bleo + CTL or Bleo + anti-TNFα, representing a biomarker for type II cell function. Quantification of expression was performed using ImageJ and represented as arbitrary unit (A.U.) and represented as mean ± SD (n = 3–6). *Significantly different (p ≤ 0.05) from other groups.