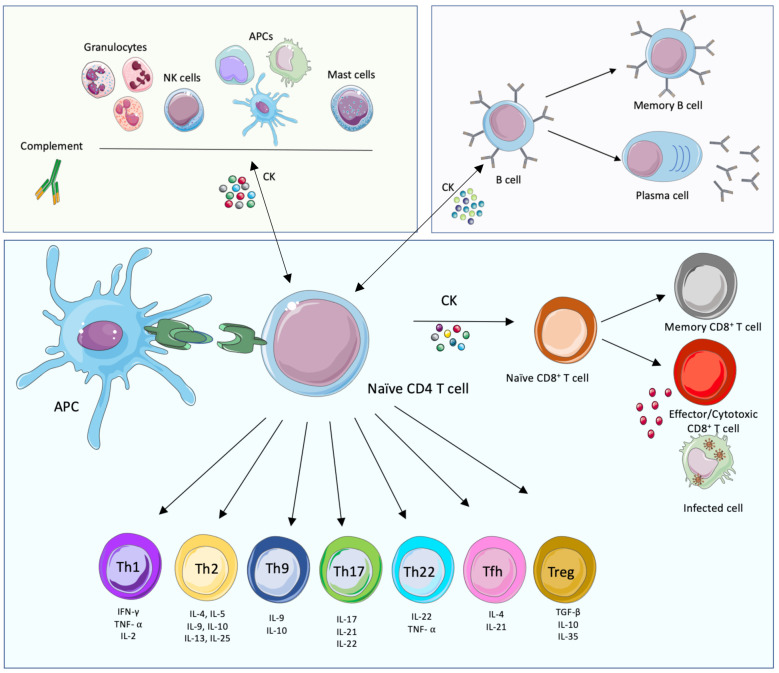
Figure 1.
Innate, humoral and cellular-mediated immune responses. The main cellular immune players of the cell-mediated innate (green background, top left), humoral (purple, top right) and adaptative cell-mediated (blue, bottom) immune responses and their interconnections are displayed. The components of the innate immune system provide, together with their effector functions and soluble mediators, an immediate response to pathogens. This response triggers in turn the adaptive immune system, mostly T cell-mediated immune responses that lead to the activation of effector T cells and the activation of B cell functions. This branch of immunity provides specific, long-lasting immune responses. The adaptive and innate immune systems are connected; importantly, while soluble mediators are important to link both arms of immunity, the presentation of foreign peptides (in green) by Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) is also necessary, together with immune mediators such as cytokines (CK). This figure was created with smart.servier.com.