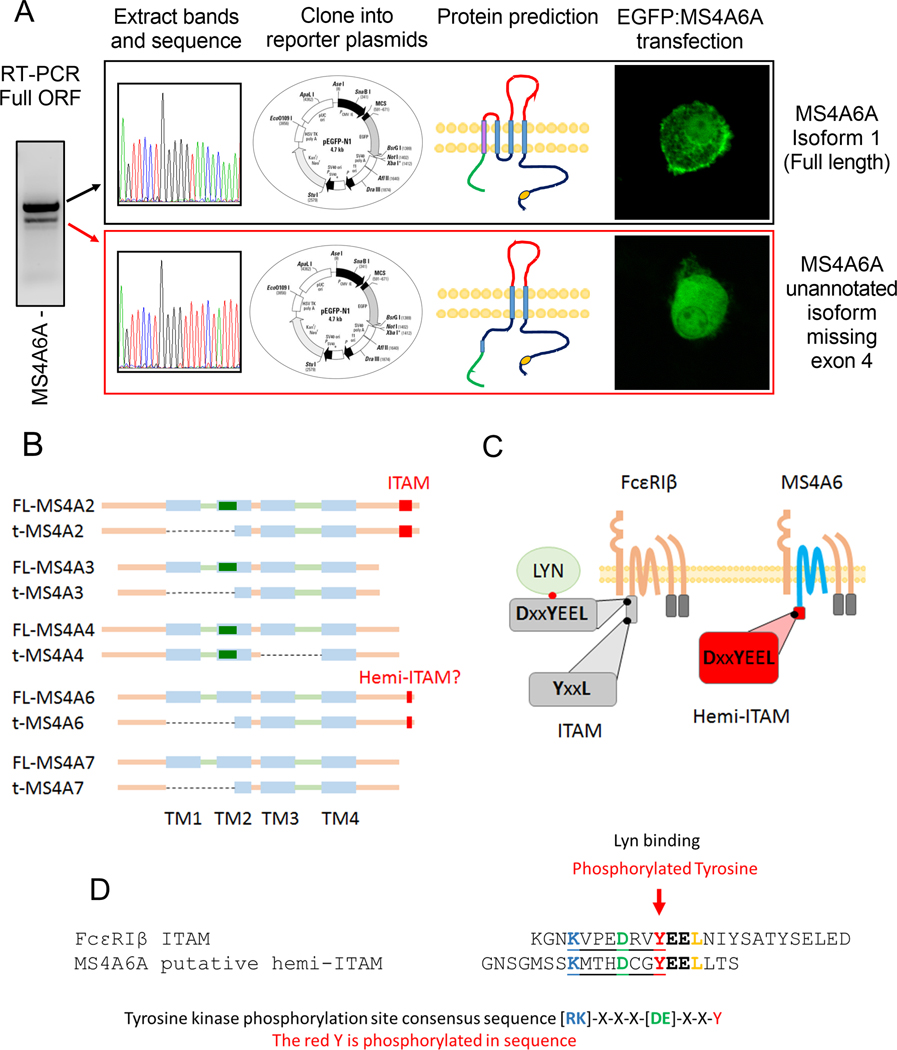
Figure 3: MS4A6A is expressed in human MCs and exhibits a similar truncation and putative signaling domain as FcεRIβ.
Amplification of the full open reading frame of the MS4A6A gene for cloning into expression plasmids confirms the presence of a truncated variant; (A) Sequencing and cloning of the two MS4A6A variants into pEGFP-N1 expression vectors provided alignment with the known isoform 1, a 4 pass transmembrane protein evident on the surface within the plasma membrane and an unannotated truncation without the first two transmembrane domains lacking surface expression; (B) Structural comparison of the full length (L) and truncated (S) variants of the MS4A gene family expressed in human mast cells. Potential caveolin-1 binding site depicted as green rectangle; (C) Graphical representation of the ITAM signaling domain of FcεRIβ indicating the tyrosine phosphorylation site where Lyn binds and the putative hemi-ITAM of MS4A6A both located on the Carboxyl-termini; (D) Peptide sequence comparison of the FcεRIβ ITAM and the putative hemi-ITAM of MS4A6A showing consensus sequences for a tyrosine kinase phosphorylation site preceding the Lyn binding site in FcεRIβ and a comparable motif in the putative MS4A6A hemi-ITAM.