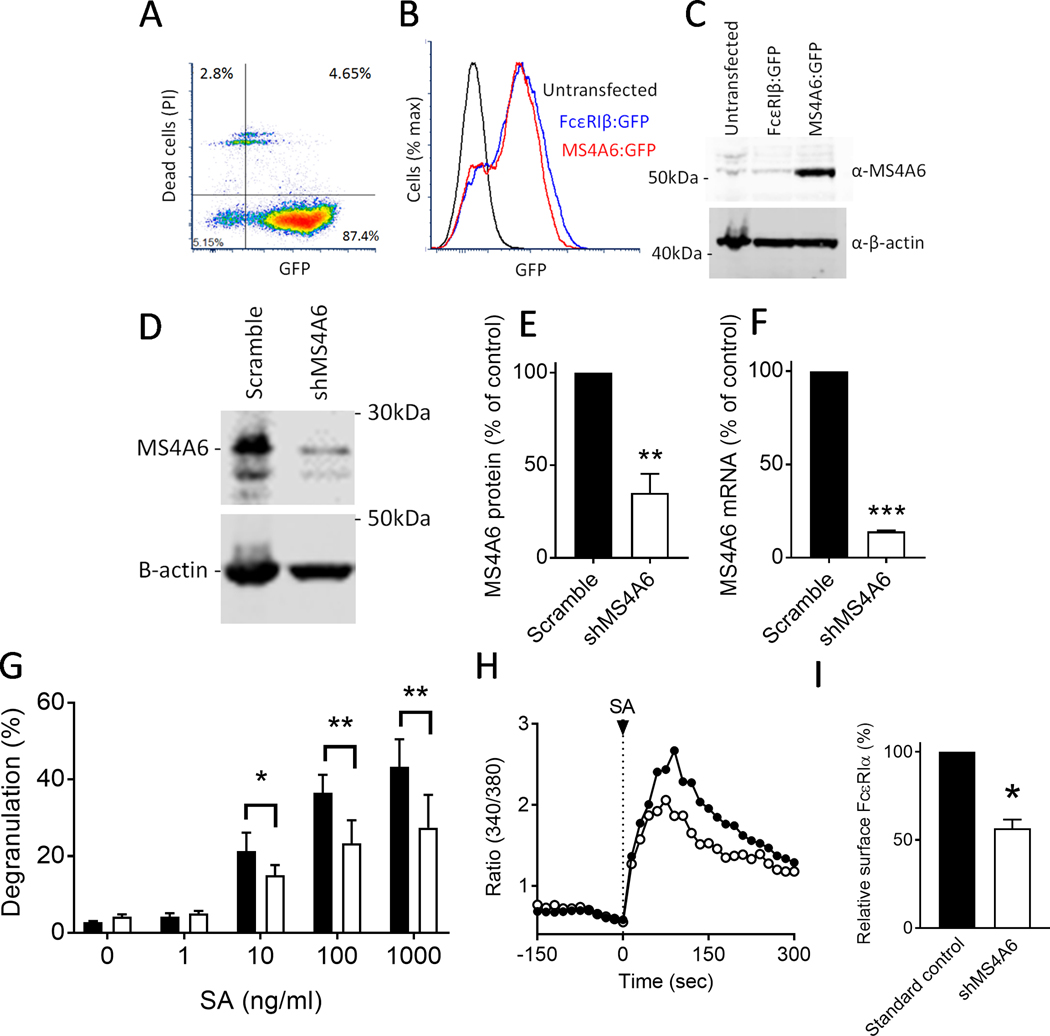
Figure 4: Knockdown of MS4A6A partially reduces degranulation and surface expression of FcεRIα.
A-D LAD2 cells were used to validate an MS4A6A antibody to determine transfection and knockdown efficiency. (A) LAD2 MCs transfected with an EGFP-MS4A6A fusion construct confirms high viability of GFP-positive cells by flow cytometry; (B) Transfection of EGFP-FcεRIβ and EGFP-MS4A6A into LAD2 MCs shows high GFP expression and transfection efficiency, which was comparable between the two constructs when compared to untransfected cells by flow cytometry; (C) Validation of an MS4A6A antibody using Western blots of cell lysates from transfected LAD2 MCs shows selectivity of the Ab for cells transfected with MS4A6A-GFP over FcεRIβ-GFP. The predicted weight of MS4A6A is 26 kDa, and GFP is 25 kDa. (D) Western blotting with the validated antibody confirms lentivirus knockdown of natively expressed MS4A6A with shRNA (predicted weight is 26 kDa); (E) Lentivirus knockdown with shMS4A6A significantly reduces protein expression by >60% compared to scramble; (F) qRT-PCR shows mRNA expression of MS4A6A is reduced by >80% after lentivirus knockdown with shMS4A6A compared to scramble; (G) Streptavidin-induced degranulation of LAD2 MCs treated with biotinylated IgE is reduced upon knockdown of MS4A6A (white) compared to scramble control (black); (H) Ratiometric calcium signaling after streptavidin stimulation at arrow shows a reduced Ca2+ response in MC with shMS4A6A knockdown (white) compared to scramble control (black). (I) Flow cytometric analysis shows surface expression of FcεRIα is significantly reduced upon shMS4A6A knockdown (white) compared to scramble control (black). Data are the mean±SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, paired t-test (E), (F) & (I), or ANOVA with post-test (G).