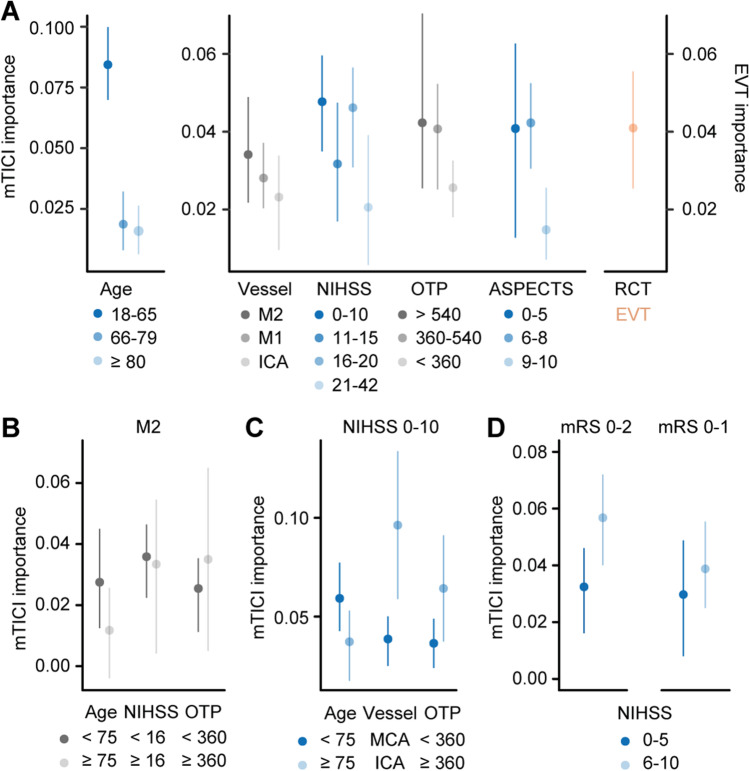
Fig. 2.
mTICI importance for outcome prediction across baseline strata in real-world data. A mTICI importance values for outcome prediction were higher in younger patients, in M2 occlusions, with lower NIHSS scores, longer onset-to-puncture times, and lower ASPECTS when compared to other subgroups of the respective strata and similar to the variable importance of EVT treatment allocation in RCT data. B In patients with M2 occlusions, mTICI importance was higher in younger patients. C In patients with lower NIHSS scores, mTICI importance was higher in ICA over MCA occlusions and with longer onset-to-puncture times. D Patients with NIHSS scores between 0 and 5 showed lower mTICI importance for outcome prediction compared to patients with NIHSS scores between 6 and 10 with a similar trend observed for the prediction of excellent outcome (mRS 0–1). A–D Conditional variable importance analyses in real-world data (GSR). Shown are the median and 5% and 95% quantiles of importance values. mTICI, modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; OTP, onset-to-puncture time; ASPECTS, Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score; M1, first segment of the middle cerebral artery; ICA, internal carotid artery; EVT, endovascular thrombectomy; RCT, randomized controlled trial; mRS, modified Rankin Scale