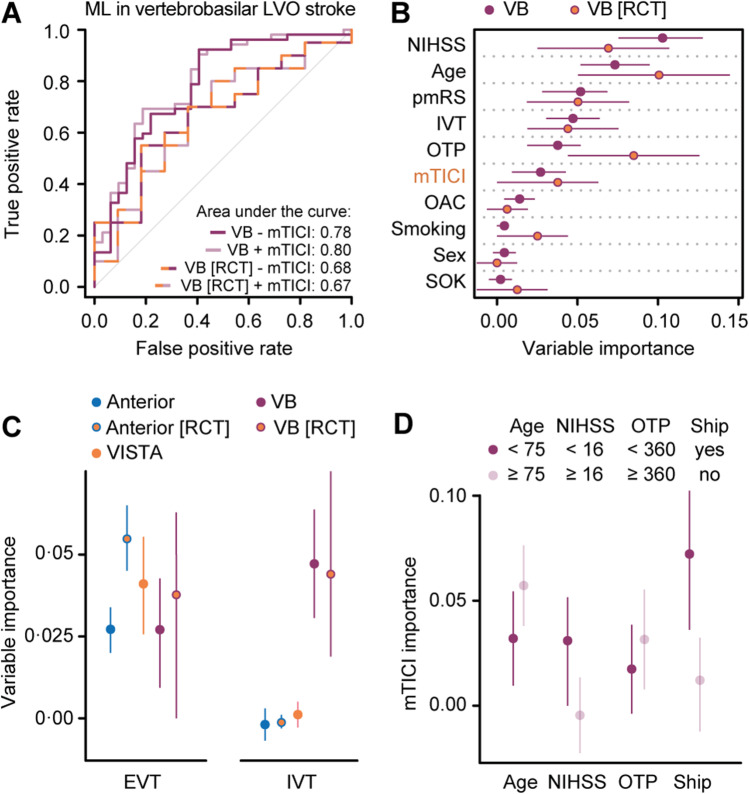
Fig. 3.
IVT treatment is more important than the mTICI score following EVT in vertebrobasilar LVO stroke. A Adding the mTICI score to pre-arterial puncture variables did not significantly improve the ML model for outcome prediction in both unselected vertebrobasilar LVO stroke patients and a selected cohort of patients complying with RCT inclusion criteria (basilar artery occlusion, NIHSS score > 9, age 18 to 85 years, onset-to-puncture time < 6 h, pmRS score 0 to 2). B Selecting real-world patients that comply with RCT inclusion criteria slightly increased the importance value of the mTICI score for outcome prediction. C While the importance values of the mTICI score for outcome prediction were similar between anterior and vertebrobasilar datasets, the IVT treatment importance value was consistently higher in vertebrobasilar compared to anterior LVO stroke. D The mTICI score importance value was higher in older patients, with lower NIHSS scores, and in patients undergoing interhospital transfer. B–D Conditional variable importance analyses in real-world data (GSR) and RCT data (VISTA, C). Shown are the median and 5% and 95% quantiles of importance values. ML, machine learning; VB, vertebrobasilar; LVO, large-vessel occlusion; RCT, randomized controlled trial; mTICI, modified Thrombolysis in Cerebral Infarction; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; OTP, onset-to-puncture time; pmRS, premorbid modified Rankin Scale; IVT, intravenous thrombolysis; OAC, oral anticoagulation; SOK, known symptom onset; EVT, endovascular treatment; ship, interhospital transfer