Fig. 1 |. Overall architecture of the EXT1–2 complex.
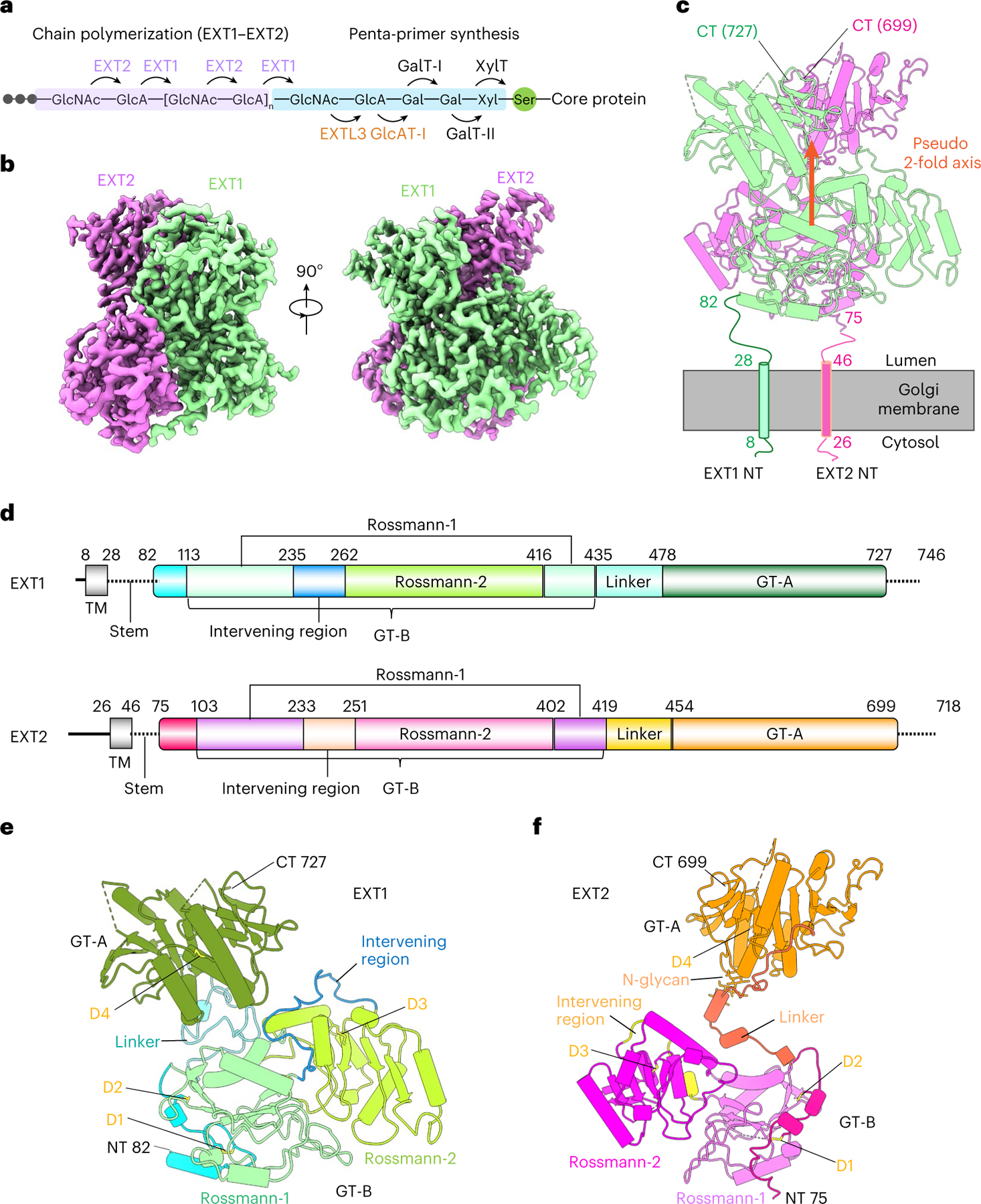
a, Sketch of HS GAG biosynthesis. The GAG is initiated by synthesis of a penta-saccharide primer linked to a serine residue in the core protein. The GAG is elongated by the alternating addition of GlcA and GlcNAc catalyzed by EXT1–2. b, Two orthogonal views of cryo-EM 3D map of EXT1–2. c, The atomic model of EXT1–2 in the cartoon is shown in its likely orientation with respect to the Golgi membrane. The truncated N-terminal transmembrane α-helices are shown as cylinders. The orange arrow indicates a pseudo two-fold symmetry axis relating EXT1 GT-B and EXT2 GT-B. d, Domain organization of EXT1 and EXT2. The intervening loop connects the Rossmann-1 and Rossmann-2 subdomains of the GT-B domain. The linker loop connects the N-terminal GT-B and the C-terminal GT-A domains. e,f, Cartoon view of the atomic models of EXT1 and EXT2 shown separately. The view is the same as in the right panel of b. Domains shown in color are the same as in d; N-glycan on EXT2 Asn637 is in sticks. D1–4 refer to the four disulfide bonds in each domain. TM, transmembrane domain.
