Extended Data Fig. 5 |. Development of an HS co-polymerase assay for EXT1–2.
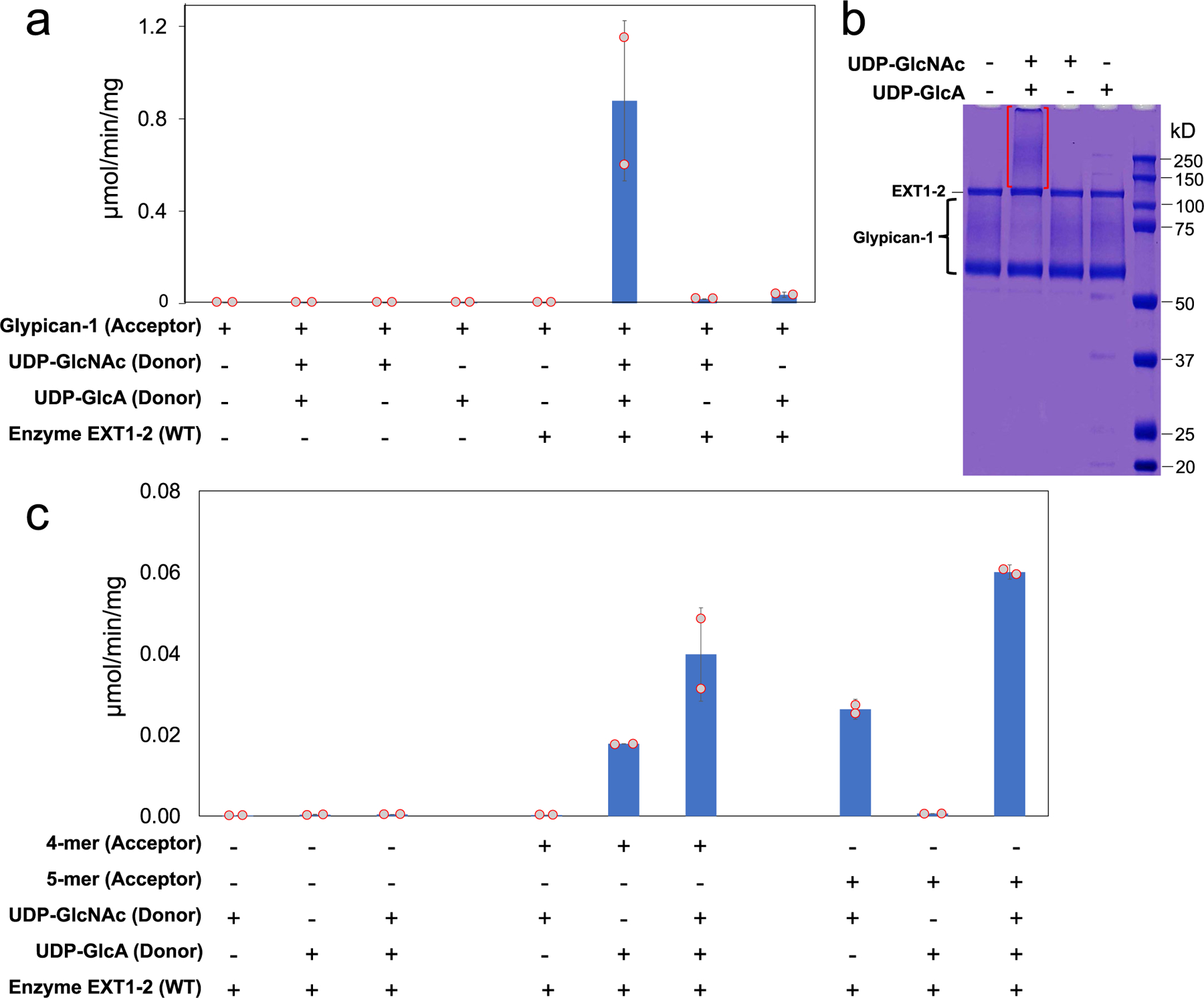
A co-polymerase assay was developed using the HS proteoglycan, glypican-1 (a and b), or heparosan primers (4-mer-pNP or 5-mer-pNP) (c) as acceptors and UDP-GlcA and UDP-GlcNAc (200 µM each) as donors. Individual assay components were tested in the reaction mixture and HS polymerization was detected using the UDP-Glo assay format (a and c). Recombinant human glypican-1 was expressed in HEK293 cells and purified for use as an acceptor substrate for HS extension of the proteoglycan. a, Low, but detectable activity was revealed when single UDP sugars were added to the reaction mix reflecting single sugar additions to the HS chains. When both UDP-GlcA and UDP-GlcNAc were added to the reaction, the enzyme activity increased ~40 fold indicating an iterative use of the sugar donors during the HS extension reaction. b, Reaction products were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining. Extended HS polymer product on glypican-1 appearing as a high molecular weight smear (red brackets) was detected only when enzyme and both sugar nucleotide donors were present in the co-polymerase reaction. The data are representative of n = 2 biologically independent samples. Original uncropped images are provided in the Source Data. c, UDP-Glo reactions using 4-mer-pNP and 5-mer-pNP as acceptors. Extension of the 4-mer primer with single sugar nucleotide donors only occurred when UDP-GlcA, but not UDP-GlcNAc, was used as donor as expected for an acceptor containing a non-reducing terminal GlcNAc residue. In contrast, extension of the 5-mer primer with single sugar nucleotide donors only occurred with UDP-GlcNAc, but not UDP-GlcA, was used as donor consistent with the presence of a non-reducing terminal GlcA residue on the acceptor. Addition of both donors in extension reactions with either the 4-mer or 5-mer as acceptor led to enhanced activity indicating an iterative use of the sugar donors during the HS extension reaction. Plots show the mean values (bar) ± s.d. (error bars) for n = 2 technical replicates (red circles).
