Figure 6. An elevation of S1P in glia or immune cells promotes neuroinflammation.
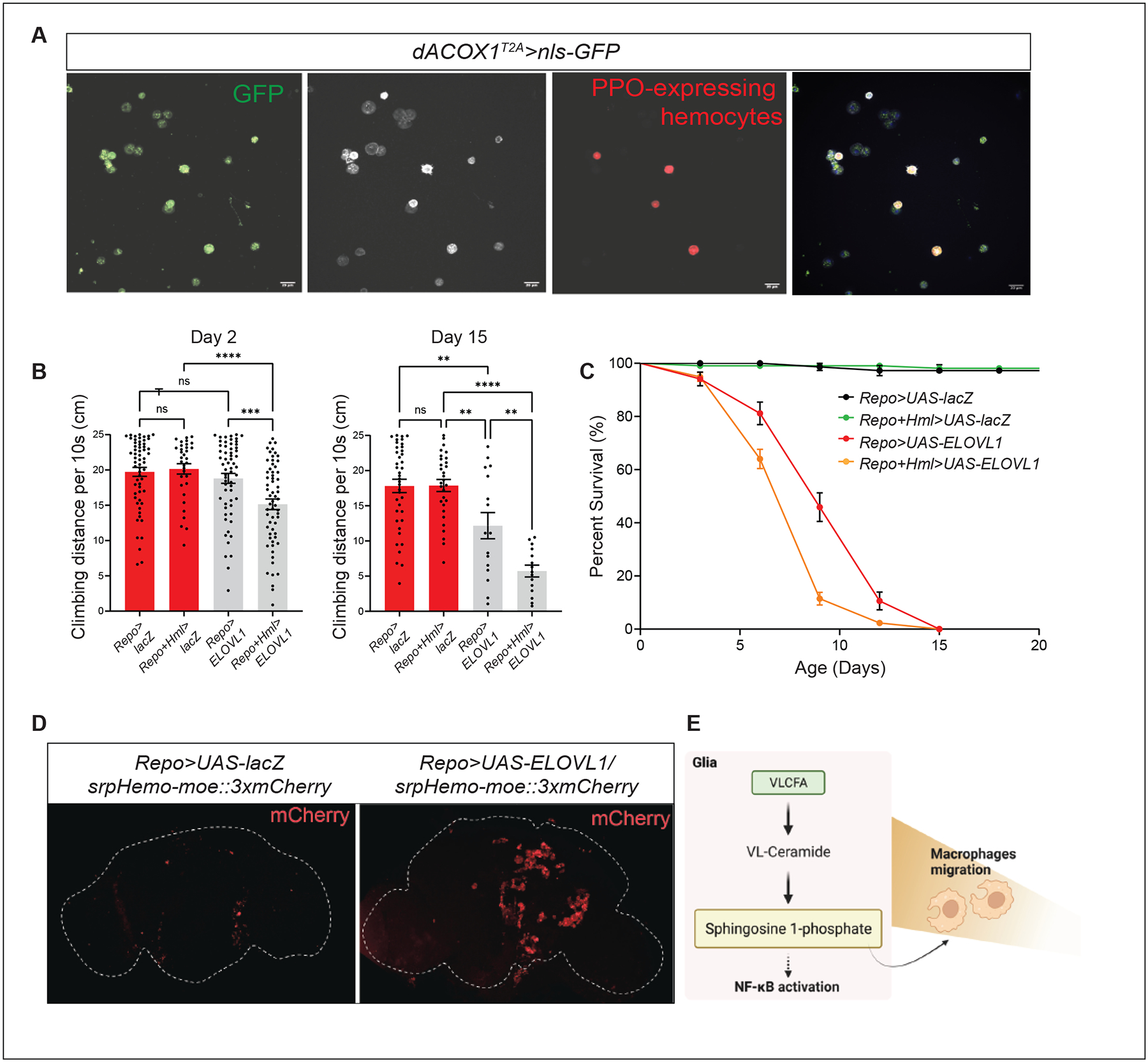
(A) dACOX1 is expressed in immune cells. Green (mCD8GFP) marks the dACOX1-expressing cells. White labels all immune cells (Hemese+). Red (BcF6-mCherry) indicates crystal cells (PPO1+). Scale bar: 20 μm. (B-C) Concurrent expression of ELOVL1 in both glia and immune cells (Repo+Hml>ELOVL1) leads to significantly enhanced progressive climbing defects on both Day 2 and 15 (n>35 per genotype) (B) and a life-span decrease (C) when compared to controls (n>50 per genotype). (D) Expression of ELOVL1 in glia (Repo>ELOVL1) induces hemocyte infiltration into the CNS when compared to control brains (Repo>UAS-LacZ). (E) Schematic showing that VLCFA accumulation leads to hemocytes recruitment into the CNS. Statistical analyses are one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey post hoc test. Results are mean ± s.e.m. (****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01; n.s., not significant).
