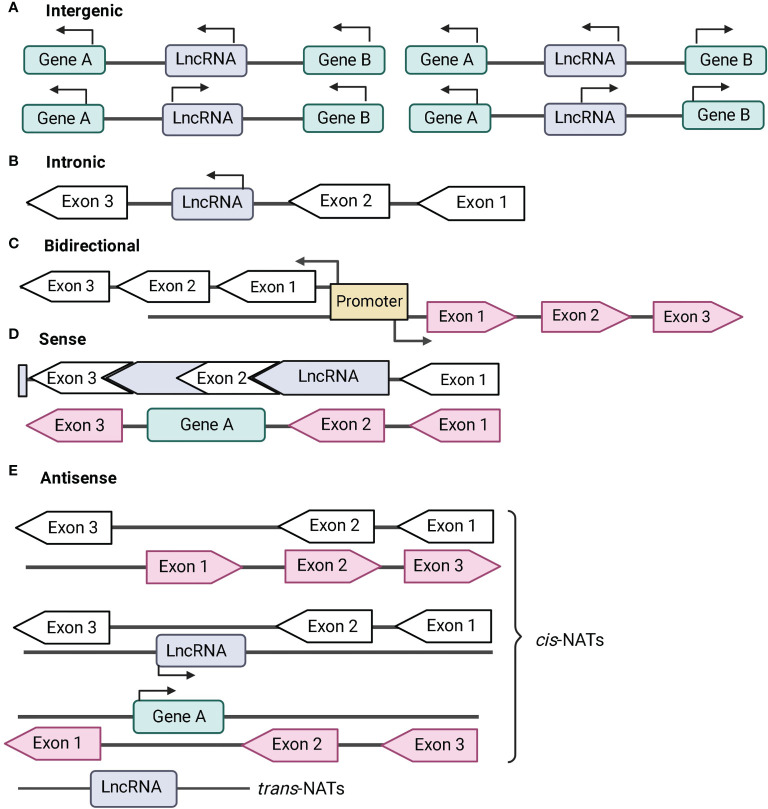
Figure 1.
Classification of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) based on genomic location. Protein-coding genes are represented in green and their exons are represented in black-bordered, arrow-shaped box. Introns are denoted by solid black lines. LncRNAs are represented in blue and their exons are represented in pink-arrow-shaped box. Direction of transcription is noted by the direction of the arrows. (A) Intergenic lncRNAs are transcribed from the intergenic regions of both the strands. (B) Intronic lncRNAs are transcribed from introns of protein-coding genes. (C) Bidirectional lncRNAs are located head-to-head with a protein-coding gene within 1 kb under a common bidirectional promoter. (D) Sense lncRNAs are transcribed from the sense strand of the protein-coding genes and contain exons from protein-coding genes. The lncRNA may partially overlap with the protein coding genes or may entirely overlap with the protein-coding gene through introns. (E) Antisense lncRNAs or naturally antisense transcripts (NATs) are transcribed from the antisense strand of protein-coding genes. NATs comprises of cis-NATs and trans-NATs. cis-NATs can overlap with exons or introns or may entirely overlap with the protein-coding sequence. trans-NATs is complementary to a target protein-coding gene and it is located in distal part of the genome.