Figure 2.
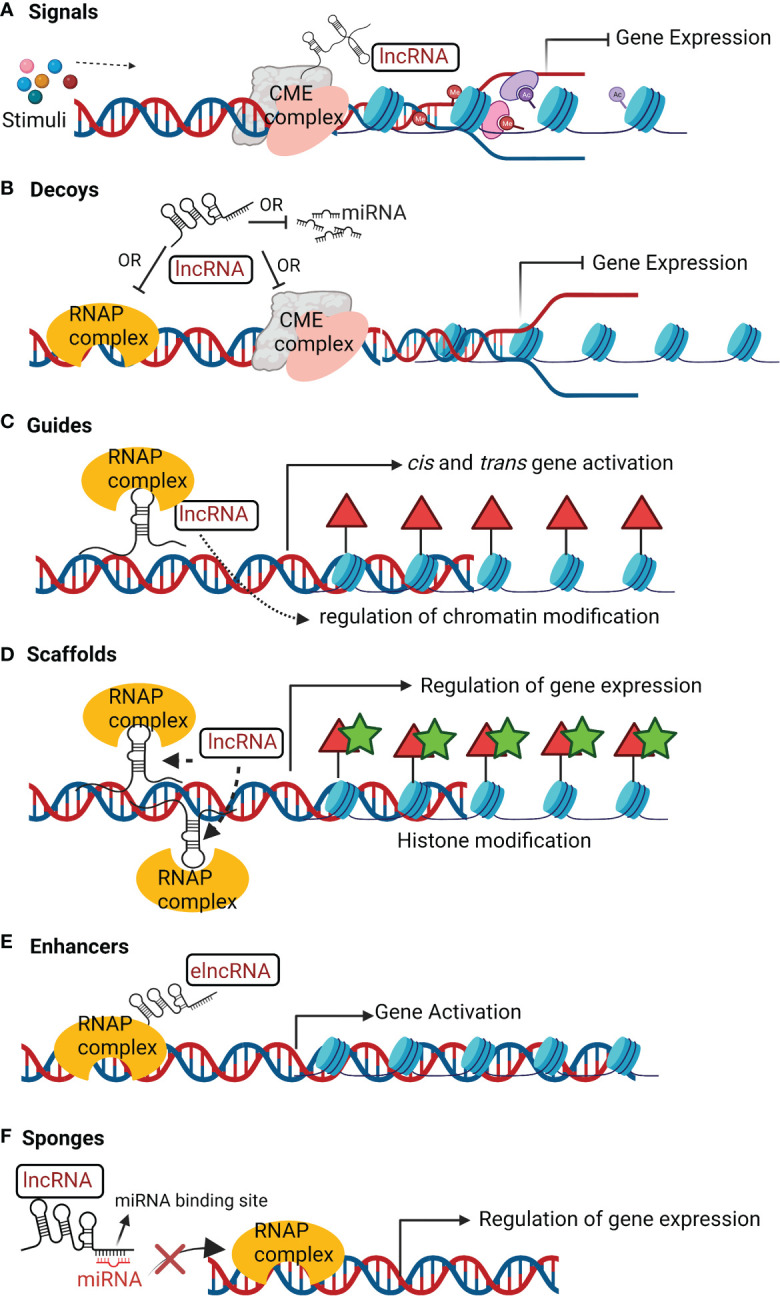
Mechanisms of action of lncRNAs. (A) Signals; lncRNAs receive a signal in response to stimuli to interact with chromatin-modifying enzyme (CME) complex to inhibit transcription. (B) Decoys; lncRNAs can interact with ribonucleoprotein (RNAP) complex or CME complex or miRNA to inhibit these regulatory factors from binding to the target gene and inhibiting its transcription. (C) Guides; lncRNAs can recruit RNAP complex and transcription factors to a specific genomic location and help to regulate chromatin arrangement for gene activation. (D) Scaffolds; lncRNAs can assemble several RNAP complex to inhibit or activate gene transcription. (E) Enhancers; enhancer lncRNA (elncRNA) enhance interaction of RNAP complex and chromatin to promote gene activation. (F) Sponges; LncRNA can act as sponges of miRNA. They have sequence complementary to miRNA and therefore can bind to miRNA, limiting its availability to transcription complex for regulation of target gene transcription.
