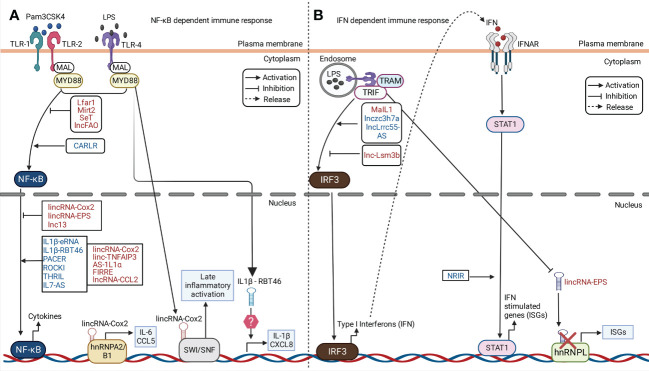
Figure 3.
LncRNA in regulation of immune response against microbial components. Examples of cytoplasmic and nuclear lncRNAs acting as positive and negative regulators of NF-κB and IFN signaling pathway in PRR dependent pathway is illustrated in the figure. Examples of murine and human lncRNAs are represented in red and blue fonts respectively. (A) In response to Pam3CSK4 or LPS stimulation, lncRNAs positively or negatively regulate the activation of NF-κB signaling via TLR-1, 2 or 4. This leads to downstream regulation of cytokines expression. For instance, lincRNA-Cox2 is upregulated in murine phagocytes. It binds to heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP)A/B and hnRNPA2/B1 leading to both the activation and repression of different genes. LincRNA-Cox2 can bind the SWItch/Sucrose non-fermentable (SWI/SNF) complex, leading to activation of late inflammatory genes. Human IL-1β-RBT46 is upregulated following LPS stimulation, which leads to enhanced expression of IL-1β and CXCL8. (B) Upon LPS stimulation, lncRNAs like MaIL1, Lnczc3h7a, and lnc-Lsm3b positively and negatively regulate the activation of Interferon (IFN) regulatory factor 3 (IFN3) which leads to subsequent regulation of IFN production. lincRNA- EPS is downregulated following LPS stimulation leading to the upregulation of IFN stimulatory genes (ISGs).