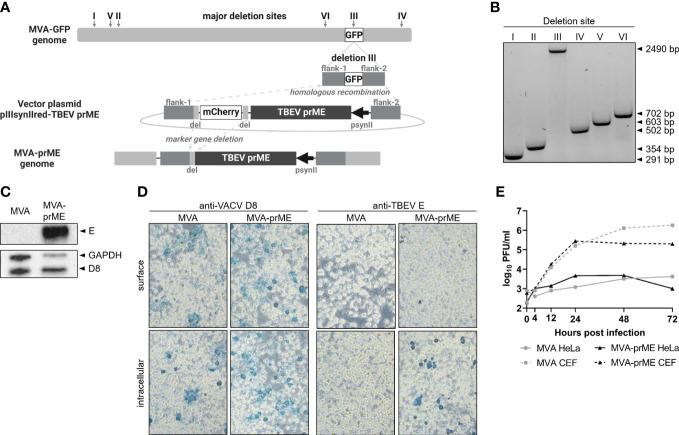
Figure 1.
Generation of MVA-prME and in vitro characterization. (A) Homologous recombination within deletion site III of MVA-GFP and pIIIsynIIred-TBEV prME as well as intragenomic homologous recombination (marker gene deletion) generated recombinant MVA expressing prME of TBEV (MVA-prME). Created with BioRender.com. (B) Separation of DNA on 1% agarose TBE gel amplified by PCRs targeting the six major deletion sites of MVA (I: 291 bp, II: 354 bp, III: 447 bp, IV: 502 bp, V: 603 bp, VI: 702 bp). Successful integration of prME in deletion site III was verified (III: 2,490 bp). (C) Expression of TBEV E protein demonstrated by Western blot on MVA-prME-infected HeLa cells (MOI 5, 24 hpi). For controls, anti-GAPDH and anti-D8 antibodies were used. (D) Immunostaining of MVA- or MVA-prME-infected HeLa cells (MOI 0.1, 24 hpi) stained against VACV D8 protein or TBEV E protein. Cells were non-permeabilized (surface) or treated with Triton X®-100 (intracellular). Images were taken with ×20 objective.(E) Growth curves of MVA- (gray) or MVA-prME (black)-infected permissive primary CEF (dotted lines) or non-permissive HeLa (solid lines) cells (MOI 0.05).