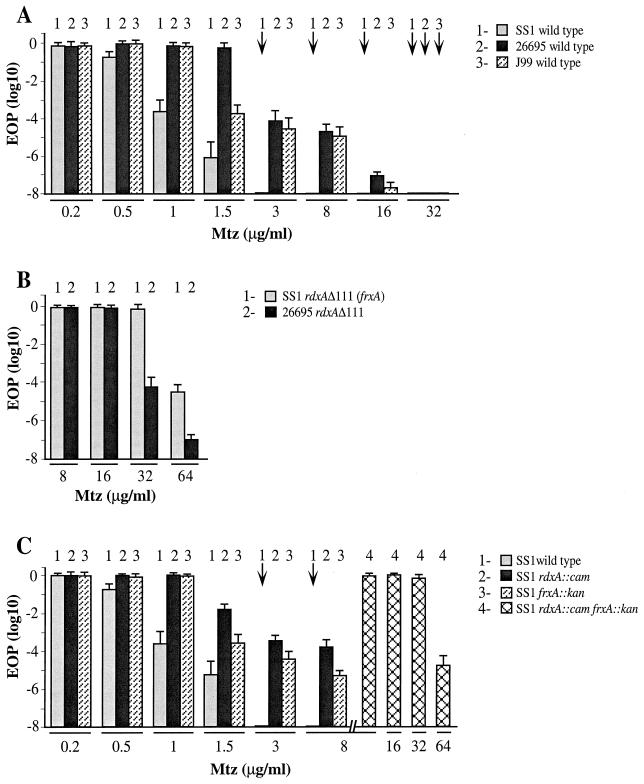
FIG. 1.
Profiles of intrinsic susceptibility and resistance to MTZ of H. pylori strains used in this study. Young, exponentially growing cultures were diluted, aliquots were spotted or spread on media with the indicated concentrations of MTZ, and colonies formed by aliquots of appropriate dilutions were counted, as detailed in Materials and Methods. Each mean and standard deviation survival value shown is based on two separate determinations from each of three young cultures, with each culture having been derived from a separate single colony isolate. (A) Strain SS1 and reference strains 26695 and J99 (references 18, 28, and 2, respectively). (B) rdxAΔ111 transformant derivatives of Mtzs strains. The designation SS1 rdxAΔ111 (frxA) refers to SS1 derivatives generated by transformation with rdxAΔ111 DNA and selection for resistance to 3 μg of MTZ per ml; these transformants were found to also contain point (frameshift) mutations in frxA. Strain 26695 rdxAΔ111 has been described previously (15) and does not contain a point mutation in frxA (J.-Y. Jeong and D. E. Berg, unpublished data). (C) Wild-type SS1 and isogenic derivatives with insertion mutations in rdxA, frxA, or both. These derivatives were generated by transformation and selection for the Camr or Kanr marker, not for Mtzr (reference 15; see also Materials and Methods). Downward arrows identify cases in which survival on MTZ-containing media was ≤10−8, relative to survival on media lacking MTZ.