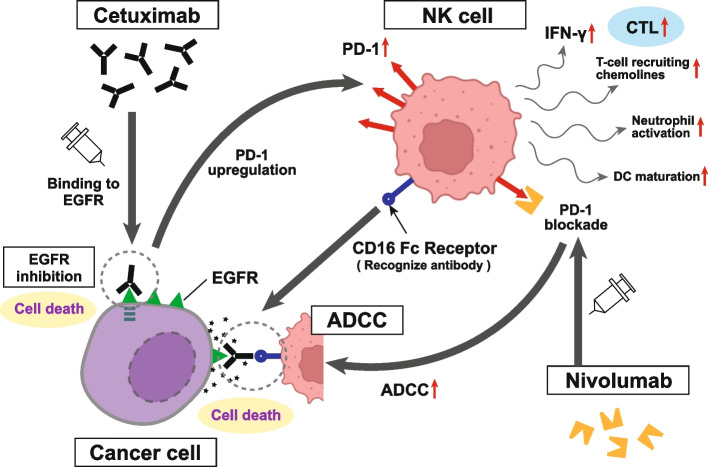
Fig. 4.
ADCC activity of cetuximab treatment and the effect on nivolumab administration. Pre-clinical studies have demonstrated the ability of cetuximab to stimulate ADCC and affect antitumor immunity. In vitro, cetuximab can mobilize NK cells, activate neutrophils, and stimulate DC maturation. This contributes to an extra antitumor effect in addition to simple EGFR inhibition. NK cell activation then produces IFN-γ, which promotes PD-L1 expression in tumor cells and emits T cell-recruiting chemokines that activate a high density of CTL in the TME. Cetuximab treatment also upregulates PD-1 expression in NK cells and maximizes antitumor effects. Additionally, PD-1 blockade increases cetuximab-mediated ADCC against PD-L1-high HNSCC cells without EGFR amplification, indicating that the combination of anti-EGFR antibodies with ICIs can enhance both innate and acquired antitumor immune responses