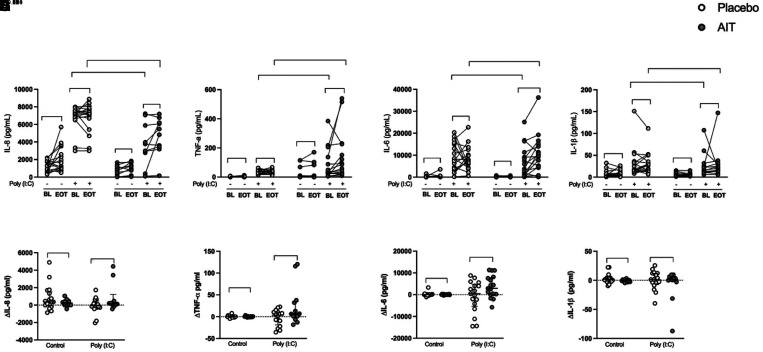
Figure 5.
House dust mite sublingual allergen immunotherapy (AIT) increased polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly(I:C))–induced human bronchial epithelial cell (HBEC) proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-α) in patients with allergic asthma. HBECs from patients with allergic asthma were stimulated with 10 μg/ml poly(I:C) for 24 hours. Cytokines were measured in cell-free supernatants using multiplex ELISA. (A–D) Protein release absolute values of IL-8 (A), TNF-α (B), IL-6 (C), and IL-1β (D). (E–H) Relative changes of protein release ([Week 24] EOT − BL) of IL-8 (E), TNF-α (F), IL-6 (G), and IL-1β (H). Relative change (Δ) values are presented as median with interquartile range; placebo (n = 17) and AIT (n = 14–17) for protein release. P values <0.05 were considered to indicate significant differences. BL = baseline; EOT = end of treatment.