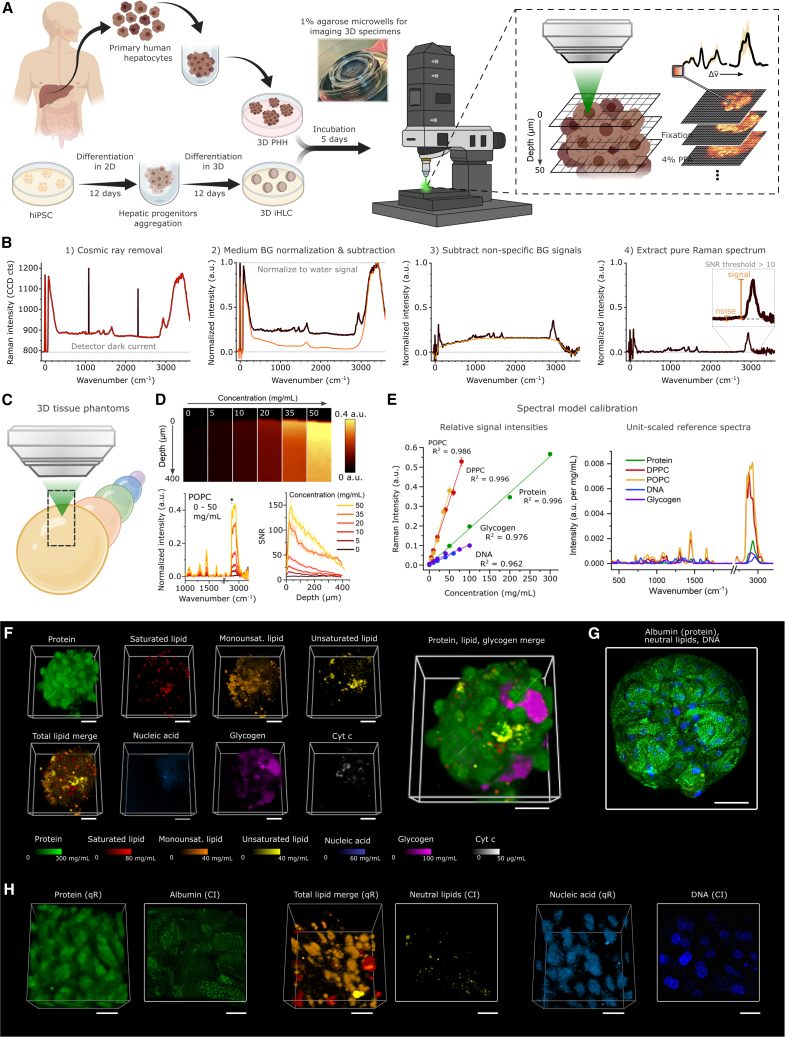
Figure 1.
qRamanomics platform for chemometric phenotyping of 3D biospecimens enables quantitative assessment of distribution, abundance, and co-localization of biomolecules
(A) Workflow for the formation and Raman analysis of 3D PHH spheroids and 3D iHLC organoids.
(B) Spectral preprocessing algorithm employing the water signal as an internal standard for all measurements.
(C) Scheme of Raman analysis of 3D biomolecular tissue phantoms of varying composition.
(D) 3D tissue phantoms with range of POPC concentrations elucidate linear range of quantitation and allow for depth-dependant signal interference studies.
(E) Signal intensities vary for each major class of biomolecules, and reference spectra are scaled accordingly to extract the unit-scaled (a.u. per 1 mg/mL) spectra for each.
(F) High-content qRamanomics imaging of the whole 3D PHH spheroid. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(G) Representative image of the whole organoid immunostaining for albumin with counterstaining of neutral lipids and DNA. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(H) High-resolution qRamanomics imaging (qR, left) and confocal imaging (CI, right) of protein, lipids, and nucleic acids in the segment of the 3D iHLC organoid. Scale bars, 20 μm.