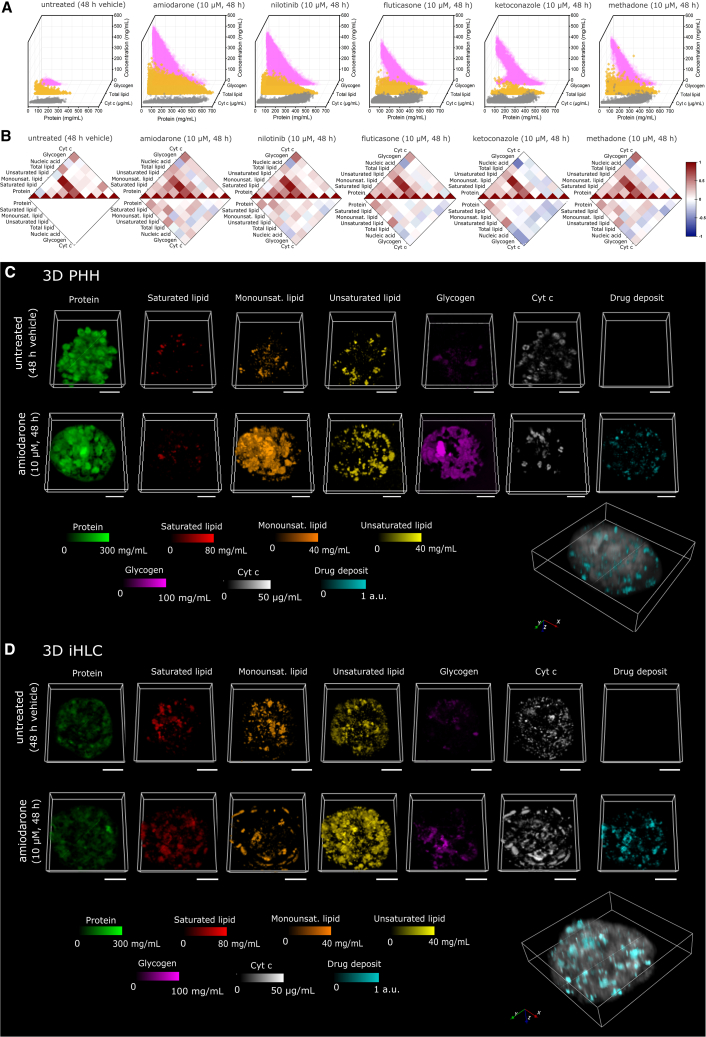
Figure 3.
qRamanomics reveals high-content compositional phenotypic changes in response to drug treatment
(A) Frequency distribution plots of total lipid, glycogen, and cytochrome c vs. protein content for representative drug-treated samples. High-content chemometric profiling of individual control (48 h of vehicle treatment).
(B) Drug-specific changes in compositional phenotype for drug-treated 3D PHHs by quantitative high-content correlation analysis (n = 4 spheroids per group). Top half of plots shows Pearson’s correlation and bottom half shows absolute difference compared with untreated control.
(C and D) untreated and amiodarone-treated (10 μM, 48 h) 3D PHH spheroids (C) and iHLC organoids (D). Amiodarone induces significant measurable changes in biomolecular composition of both 3D liver representations. Scale bars, 50 μm. 3D renderings of amiodarone and metabolites deposits (shown in cyan) detected in PHH spheroids and iHLC organoids. The biomolecular matrix (i.e., protein, total lipid, and glycogen) was combined and is shown in gray (arbitrary intensity units) to reveal clear distinction between endogenous biomolecules and xenobiotic compounds present in specimens.