Abstract
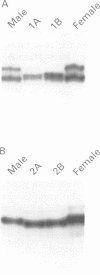
Hypospadias is a common urological abnormality and may occur in simple (glandular or penile) or severe forms (perineal). Perineal hypospadias often occurs in association with other genital abnormalities, such as bilateral cryptorchidism and micropenis, and may be the result of partial androgen insensitivity. We have investigated the androgen binding status and androgen receptor gene of boys from two unrelated families. The first pair of brothers had partial androgen insensitivity with perineal hypospadias, bilateral cryptorchidism, and micropenis, while the other boys had isolated perineal hypospadias. Qualitative androgen binding defects were shown in both sets of brothers and different point mutations of the androgen receptor gene were found in the two families. These findings suggest that the genital abnormalities in the affected brothers result from defects in the androgen receptor. Furthermore, severe familial hypospadias may be a previously unrecognised part of the phenotypic spectrum of the partial androgen insensitivity syndrome. This study provides valuable information for the genetic counselling of families affected by this X linked genital abnormality.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batch J. A., Williams D. M., Davies H. R., Brown B. D., Evans B. A., Hughes I. A., Patterson M. N. Androgen receptor gene mutations identified by SSCP in fourteen subjects with androgen insensitivity syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Oct;1(7):497–503. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.7.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T. Molecular cloning of human and rat complementary DNA encoding androgen receptors. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):324–326. doi: 10.1126/science.3353726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A., Hammond H. A., Jin L., Caskey C. T., Chakraborty R. Genetic variation at five trimeric and tetrameric tandem repeat loci in four human population groups. Genomics. 1992 Feb;12(2):241–253. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans B. A., Jones T. R., Hughes I. A. Studies of the androgen receptor in dispersed fibroblasts: investigation of patients with androgen insensitivity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1984 Jan;20(1):93–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1984.tb00063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans B. A., Williams D. M., Hughes I. A. Normal postnatal androgen production and action in isolated micropenis and isolated hypospadias. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Sep;66(9):1033–1036. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.9.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart J. P., Linhard H. R., Berkovitz G. D., Jeffs R. D., Brown T. R. Androgen receptor levels and 5 alpha-reductase activities in preputial skin and chordee tissue of boys with isolated hypospadias. J Urol. 1988 Nov;140(5 Pt 2):1243–1246. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)42014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. L. Genetic epidemiology of hypospadias. Epidemiol Rev. 1990;12:29–40. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes I. A., Evans B. A. Androgen insensitivity in forty-nine patients: classification based on clinical and androgen receptor phenotypes. Horm Res. 1987;28(1):25–29. doi: 10.1159/000180921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenster G., van der Korput H. A., van Vroonhoven C., van der Kwast T. H., Trapman J., Brinkmann A. O. Domains of the human androgen receptor involved in steroid binding, transcriptional activation, and subcellular localization. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1396–1404. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubahn D. B., Brown T. R., Simental J. A., Higgs H. N., Migeon C. J., Wilson E. M., French F. S. Sequence of the intron/exon junctions of the coding region of the human androgen receptor gene and identification of a point mutation in a family with complete androgen insensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9534–9538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubahn D. B., Joseph D. R., Sullivan P. M., Willard H. F., French F. S., Wilson E. M. Cloning of human androgen receptor complementary DNA and localization to the X chromosome. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.3353727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelli M., Tilley W. D., Wilson C. M., Griffin J. E., Wilson J. D., McPhaul M. J. Definition of the human androgen receptor gene structure permits the identification of mutations that cause androgen resistance: premature termination of the receptor protein at amino acid residue 588 causes complete androgen resistance. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1105–1116. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. J., Lloyd S. Observations on the epidemiology of simple hypospadias. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 31;1(5856):768–770. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5856.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweikert H. U., Schlüter M., Romalo G. Intracellular and nuclear binding of [3H]dihydrotestosterone in cultured genital skin fibroblasts of patients with severe hypospadias. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):662–668. doi: 10.1172/JCI113930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simental J. A., Sar M., Lane M. V., French F. S., Wilson E. M. Transcriptional activation and nuclear targeting signals of the human androgen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):510–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleddens H. F., Oostra B. A., Brinkmann A. O., Trapman J. Trinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the androgen receptor gene (AR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1427–1427. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1427-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]