Fig. 5. Cellular and biochemical studies of ALK compound mutations.
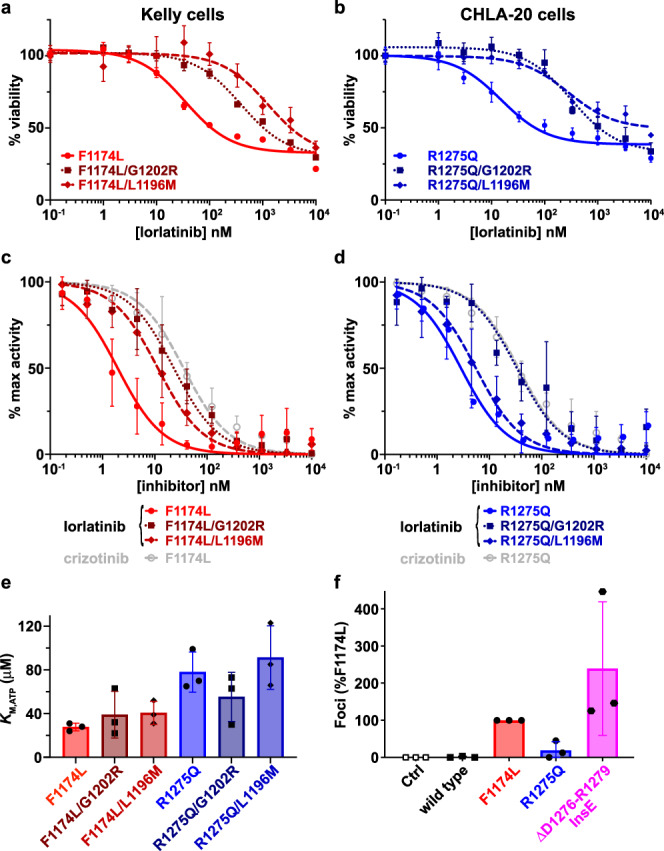
a Cell viability assays at different lorlatinib concentrations of Kelly cells harboring either the single parental ALK F1174L driver mutation (red circles, solid curve) or the compound mutations F1174L/L1196M (medium red diamonds, dashed curve), or F1174L/G1202R (dark red squares, dotted curve) introduced in cis using CRISPR. b Cell viability assays at different lorlatinib concentrations of CHLA-20 neuroblastoma cells harboring either the single parental ALK R1275Q mutation (blue circles, solid curve) or the compound mutation F1174L/G1202R (dark blue squares, dotted curve). Data are plotted as the mean ± SD of three biological replicates, each performed in technical triplicate. c Comparison of in vitro inhibition of purified ALK-TKD for different F1174L-based variants. IC50 values for F1174L-mutated ALK-TKD were assessed for lorlatinib (red circles, solid red curve: IC50 = 2.3 ± 1.1 nM) and crizotinib (open gray circles, dashed gray curve: IC50 = 40 ± 20 nM), and compared with lorlatinib IC50 values for F1174L/L1196M (medium red diamonds, dashed curve: IC50 = 12 ± 6.2 nM) and F1174L/G1202R (dark red squares, dotted curve: IC50 = 26 ± 16 nM). d Comparison of in vitro inhibition of ALK-TKD for different R1275Q-based variants. IC50 values for R1275Q-mutated ALK-TKD were assessed for lorlatinib (blue circles, solid blue curve: IC50 = 2.9 ± 0.8 nM) and crizotinib (open gray circles, dashed gray curve: IC50 = 38 ± 24 nM), and compared with lorlatinib IC50 values for R1275Q/L1196M (medium blue diamonds, dashed curve: IC50 = 8 ± 5.2 nM) and R1275Q/G1202R (dark blue squares, dotted curve: IC50 = 40 ± 21 nM). e Measured KM,ATP values for different ALK-TKD variants, with numbers tabulated in Supplementary Table 1. f Focus formation assay results for ΔD1276-R1279InsE ALK (magenta) compared with wild-type (black), F1174L (red), and R1275Q (blue). Data are plotted as the mean ± SD of three biological replicates, each performed in technical duplicate. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
