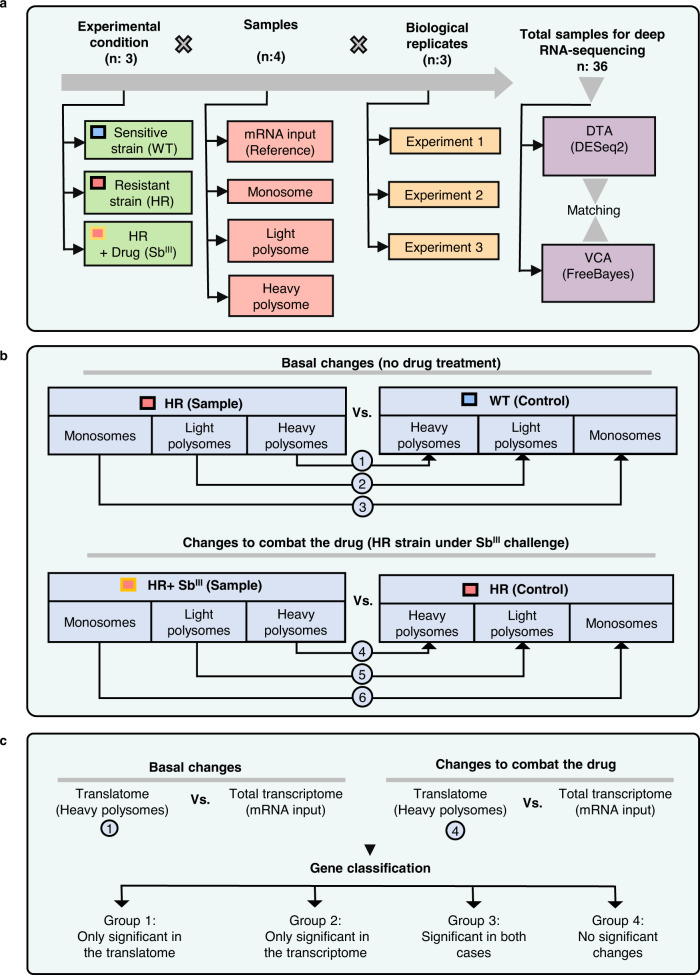
Fig. 2. Schematic representation of the experimental design.
a Experimental conditions. Three experimental conditions were tested: WT and HR strains growing without drug challenge, and HR strains growing under drug challenge. Four types of samples were evaluated per experimental condition (input, monosome, light polysomes, and heavy polysomes). The experiment was done in three biologically independent replicates. A total of 36 (3X4X3 = 36) samples were used for RNA-seq followed by bioinformatic analysis. DESeq2 algorithm was used for differential translational analysis (DTA). Variant calling analysis (VCA) was used to detect gene variants exclusively present in HR strain using the FreeBayes algorithm. Then, the two bioinformatic analyses were matched based on the affected genes. b Detailed strategy for differential translational analysis (DTA) to estimate the basal changes in the translatome after the selection for drug resistance (basal changes), and changes associated with active drug resistance (changes to combat the drug). A total of six dual comparisons were performed including monosomes, and light and heavy polysomes. c Differential expression analyses were independently performed to identify changes in the total transcriptome (total mRNA used as input for polysome profiling) and translatome (heavy polysomes fraction). The identified genes were matched and classified into four groups. Group 1: genes that were detected as differentially expressed only in heavy polysomes. Group 2: genes that were detected as differentially expressed only in the total transcriptome. Group 3: genes that were detected as differentially expressed in both total transcriptome and heavy polysomes. Group 4: genes that were not differentially expressed.