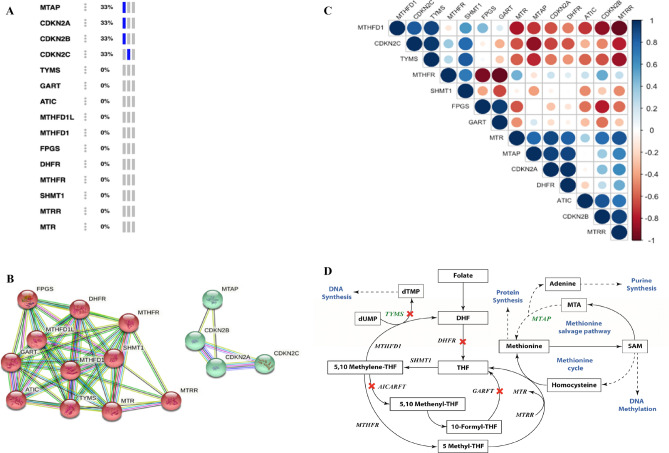
Figure 1.
Folate pathway genes and pemetrexed targets. (A) Genetic alteration (deep deletion) of specific genes in Chordoma accessed using cBioPortal. Out of the three samples, samples with deep deletion are shown in blue and samples without any deep deletion are shown in grey (B). Protein–protein interaction network obtained using STRING database. Edges represent protein–protein associations—blue and pink lines show known interactions from curated databases and experimentally determined interactions respectively; green (gene neighborhood), red (gene fusions) and blue (gene co-occurrence) lines show predicted interactions; light green lines denote text mining, black lines denote co-expression and light purple lines denote protein homology. (C). Expression correlation analysis of Chordoma samples obtained from Array Express dataset E-MEXP-353. Correlation values range from 1 to − 1. Positive correlations are shown in shades of blue and negative correlations are shown in shades of red depending on the correlation value. (D). Folate metabolism pathway and its link to MTAP. Folate gets metabolized to form DHF and then THF by DHFR. THF gets converted to 5,10-Methylene THF and then 5-Methyl THF. 5-Methyl THF gets converted back to THF by MTR. In a parallel process homocysteine gets converted to methionine. Methionine is at the core of methionine salvage pathway and the methionine cycle. MTAP metabolizes MTA through the methionine salvage pathway producing methionine and adenine required for protein synthesis and purine synthesis respectively. Methionine gets converted to SAM and homocysteine through a series of steps in the methionine cycle. TYMS is involved in conversion of dUMP to dTMP leading to DNA synthesis process. Targets of pemetrexed are marked by a red cross. The key genes TYMS and MTAP are highlighted in green. Cellular processes and metabolism pathways are shown in blue. Dashed arrows represent series of intermediate steps. MTAP methylthioadenosine phosphorylase; CDKN2A cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; CDKN2B cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2B; CDKN2C cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2C; TYMS thymidylate synthetase; FPGS folylpolyglutamate synthase; DHF dihydrofolate; THF tetrahydrofolate; ATIC 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase/IMP cyclohydrolase; GART phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase, phosphoribosylglycinamide synthetase, phosphoribosylaminoimidazole synthetase; MTHFD1 methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, cyclohydrolase and formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase 1; DHFR dihydrofolate reductase; MTHFR methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; SHMT1 serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1; MTRR 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase reductase; MTR 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase; SAM S-adenosyl methionine; MTA Methylthioadenosine.