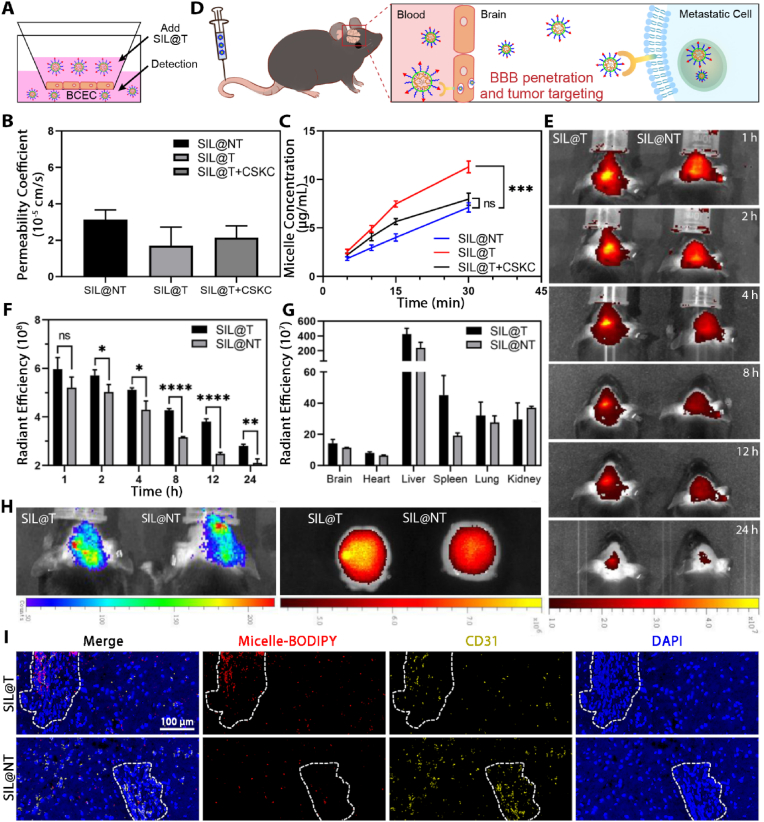
Fig. 3.
BBB penetration ability and targeting performance of SIL@T. A) Scheme of construction of the BBB model in vitro. B) Permeability of the BBB constructed in vitro (n = 3). C) BBB penetration results of micelles under different conditions. Results are reported as mean ± SD (n = 3, One-way ANOVA, ***P < 0.001). D) Scheme of SIL@T penetrating BBB and targeting metastatic tumors. E) IVIS imaging results of BM-mice at different time after tail vein injection of BODIPY-labeled micelles. F) Quantitative results in panel E (n = 3, One-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001). G) Tissue distribution of micelles 24 h after tail vein injection of BODIPY-labeled micelles (n = 3). H) Bioluminescence imaging of BM-mice and brain distribution of BODIPY-labeled micelles 24 h after tail vein injection. I) Fluorescence imaging of brain frozen sections of BM-mice 2 h after tail vein injection of BODIPY-labeled micelles. Blue: nucleus; yellow: new blood vessels; red: micelles. Scale bar: 100 μm.