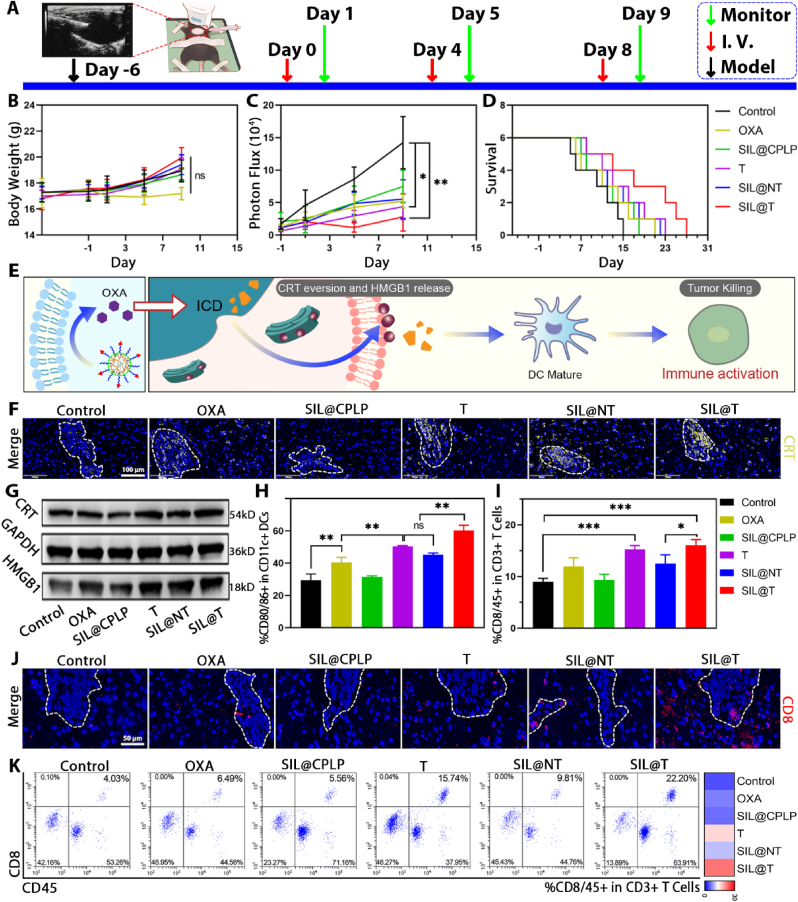
Fig. 5.
SIL@T can induce ICD, activate immune response, inhibit the growth of metastatic tumors in BM-mice and prolong the survival of BM-mice. A) Treatment and monitor schedule for SIL@T therapy. B) The change curve of body weight after administration of different preparations (n = 6). C) The signal change curve of metastasis tumor after administration of different preparations (n = 4, One-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). D) Survival curves of BM-mice after administration of different formulations (n = 6). E) Scheme of SIL@T activating an immune response. F) Immunofluorescence imaging of CRT in brain cryosections of BM-mice. Blue: nucleus; yellow: CRT. Scale bar: 100 μm. G) WB imaging of metastatic CRT and HMGB1 protein. H) Flow cytometry results of DC maturation in the cervical lymph node of BM-mice (n = 3, One-way ANOVA, **P < 0.01). I) Flow cytometry results of T cell polarization in the spleen of BM-mice (n = 3, One-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001). J) Immunofluorescence imaging of CD8+ T cell infiltration in brain cryosections of BM-mice. Blue: nucleus; red: CD8. Scale bar: 50 μm. K) Flow cytometry analysis of T cell polarization in brain metastases.