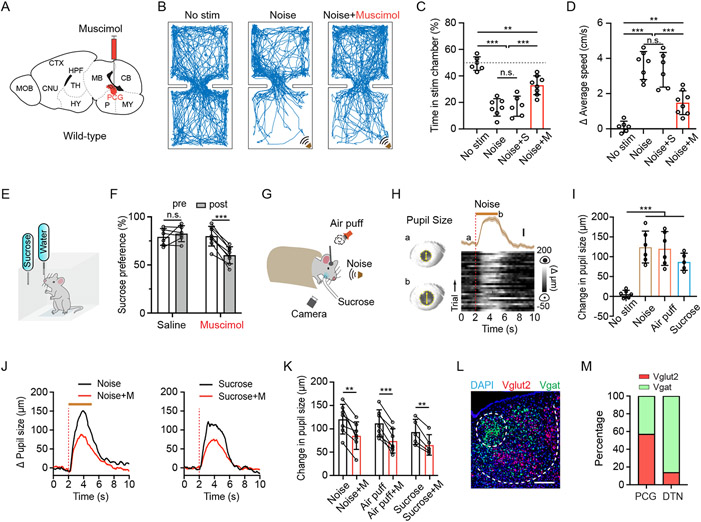
Figure 1. PCG mediates sensory-induced aversion and reward-related behavior.
(A) Schematic of a sagittal section of the mouse brain and infusion of fluorescent muscimol into PCG.
(B) Example movement tracking traces in the place preference test for three mice in no-stimulation, noise alone (80 dB SPL), and noise plus PCG silencing (with muscimol) conditions.
(C) Summary of percentage time spent in the stimulation chamber in different conditions. N = 6, 7, 6, 8 respectively. Gray dash line marks 50% level. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA. “n.s.”, not significant. S, saline. M, muscimol.
(D) Summary of average locomotion speed in the stimulation chamber. N = 6, 7, 6, 8 respectively. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA.
(E) Schematic of sucrose preference test.
(F) Summary of sucrose preference in the saline control and PCG silencing groups. N = 6 and 8 respectively. Sucrose preference was quantified as the relative amount of sucrose water consumption during a 1-hr test session (see Method). ***P < 0.001, paired t-test.
(G) Experimental configuration for measuring pupil size changes in responding to noise, air puffs or sucrose water (5%) delivery in awake head-fixed condition.
(H) Plot of pupil size changes in responding to noise (70 dB SPL, 3-s duration) for an example naïve animal. Left, example images of pupil during baseline (a) and dilated (b) conditions. Yellow arrows mark the pupil diameter. Right, plot of average change in pupil size (mean ± SEM) aligned to onset of noise stimulation (top) and Δ pupil size in each of 30 trials (bottom) for an example animal. Dotted red line indicates stimulus onset. Brown bar indicates the duration of noise.
(I) Summary of peak pupil size changes in no-stimulation, noise, air puffs and sucrose water delivery groups. N = 6, 6, 6, 5 respectively. ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA.
(J) Plot of average pupil size changes in responding to noise (left) or sucrose water (right) before (black) and after (red) silencing PCG with muscimol for an example mouse. Red dotted line indicates the onset time of stimulus. Brown bar indicates the duration of noise.
(K) Summary of peak pupil size changes in responding to different sensory stimuli before and after silencing PCG with muscimol. N = 7, 7, 5 respectively. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, paired t-test.
(L) Representative RNAscope staining in PCG for the Vglut2 (red, Slc17a6) and Vgat (green, Slc32a1). Blue represents DAPI staining. Scale, 200 μm.
(M) Relative abundance of Vglut2+ (red) vs. Vgat+ (green) neurons. For each brain structure, n = 4 animals.
Error Bar = SD in all plots.