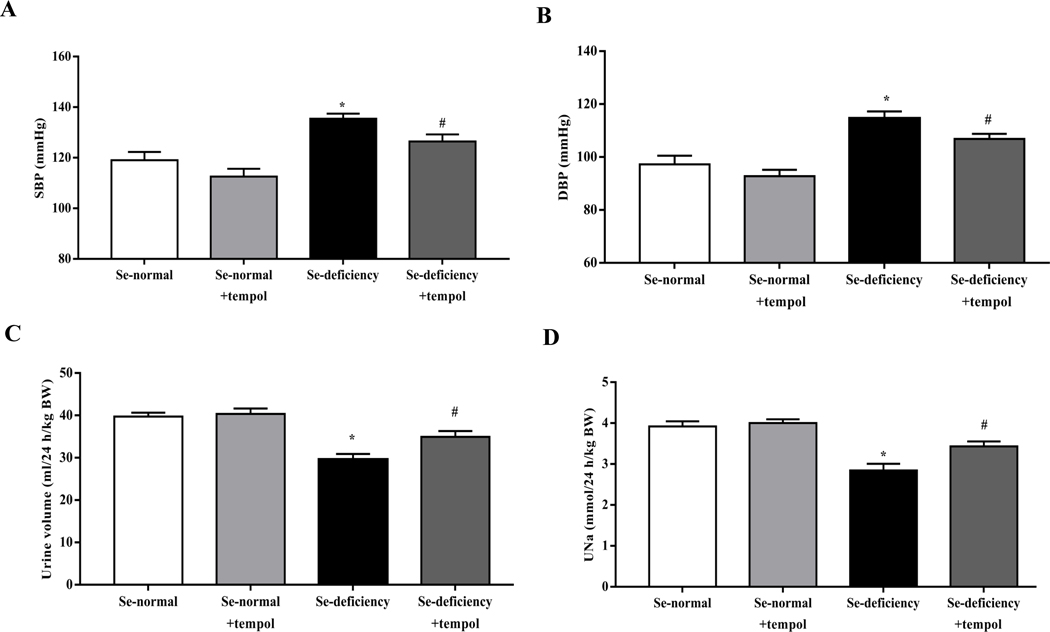
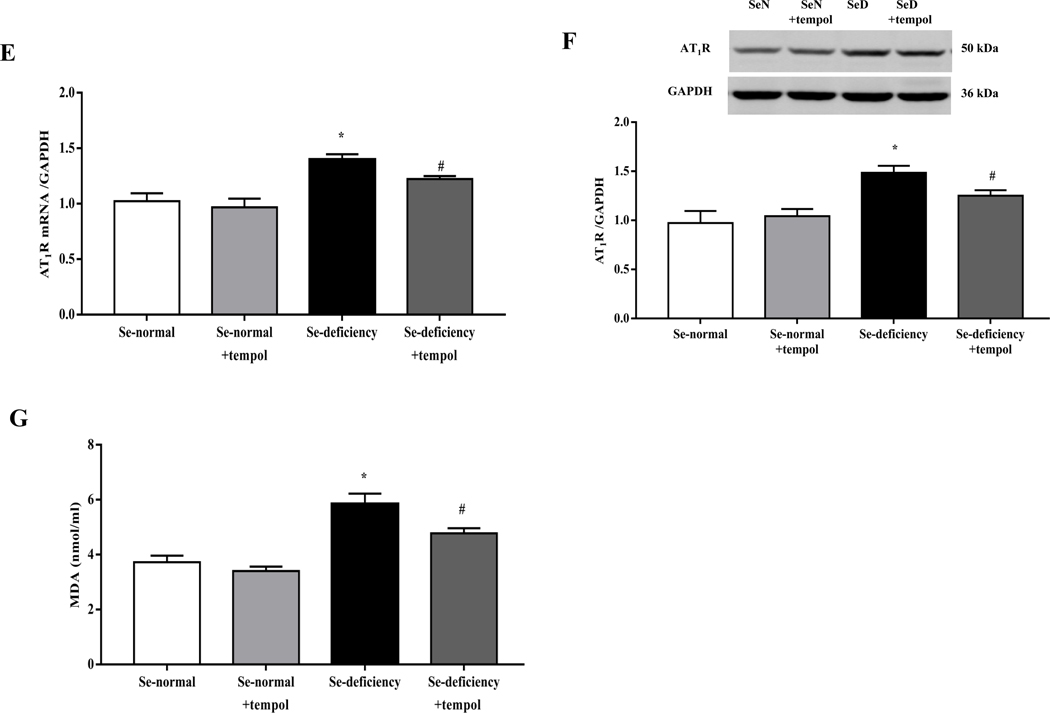
Fig. 5. Effects of tempol in the regulation of blood pressure and sodium excretion in selenium-deficient rats.
After feeding the indicated diet for 12 weeks, selenium-deficient rats or selenium-normal rats were then treated with tempol (1 mM) for 4 weeks. (A, B) Systolic- (SBP, A) and diastolic blood pressures (DBP, B) in selenium-deficient rats treated with tempol (*P < 0.05 vs Se-normal; #P < 0.05 vs Se-deficiency, n=5/group). (C, D) 24-hours urine volume (C) and urine sodium excretion (UNa, D) in selenium-deficient rats treated with tempol (*P < 0.05 vs Se-normal; #P < 0.05 vs Se-deficiency, n=5/group). (E, F) The mRNA (E) and protein expression (F) of AT1R in selenium-deficient rats treated with tempol (*P < 0.05 vs Se-normal; #P < 0.05 vs Se-deficiency, n=5/group). (G) Effect of tempol in the serum MDA levels in selenium-deficient rats (*P < 0.05 vs Se-normal; #P < 0.05 vs Se-deficiency, n=5/group).