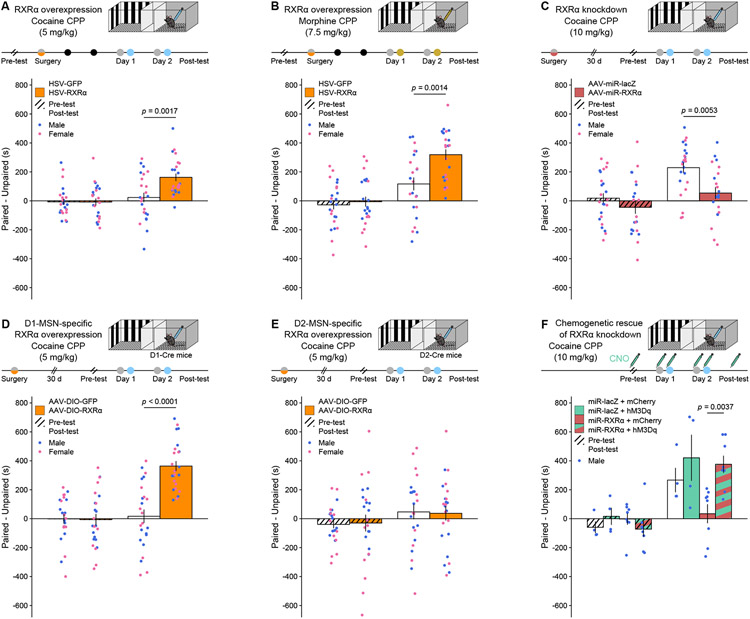
Figure 5. RXRα bidirectionally and cell-type-specifically regulates dose sensitivity in drug-reward associative learning.
(A) HSV-mediated RXRα overexpression in NAc increased conditioned place preference (CPP) for a subthreshold (5 mg/kg) dose of cocaine (LMM-ANOVA: interaction Test:Virus: F1,44 = 10.1557, p = 0.002647, followed by Sidak’s post hoc tests).
(B) HSV-mediated RXRα overexpression in NAc increased CPP for a 7.5 mg/kg dose of morphine (LMM-ANOVA: interaction Test:Virus: F1,43 = 9.4374, p = 0.003681, followed by Sidak’s post hoc tests).
(C) AAV-mediated RXRα knockdown in NAc decreased CPP for a high (10 mg/kg) dose of cocaine (LMM-ANOVA: interaction Test:Virus: F1,41 = 5.1204, p = 0.02901, followed by Sidak’s post hoc tests).
(D) AAV-mediated NAc D1-MSN-specific RXRα overexpression increased CPP for a subthreshold (5 mg/kg) dose of cocaine (LMM-ANOVA: interaction Test:Virus: F1,44 = 28.4447, p < 0.0001, followed by Sidak’s post hoc tests).
(E) AAV-mediated NAc D2-MSN-specific RXRα overexpression did not increase CPP for a subthreshold (5 mg/kg) dose of cocaine (LMM-ANOVA: interaction Test:Virus: F1,44 = 0.0813, p = 0.7768).
(F) Chemogenetic activation of NAc MSNs using the hM3Dq DREADD rescued the effects of RXRα knockdown on cocaine CPP at a high (10 mg/kg) dose (LMM-ANOVA: interaction Test:DREADD:knockdown F1,20 = 5.4961, p = 0.0295, followed by Sidak’s post hoc tests).
Both male and female mice were used in all experiments except for chemogenetics (n = 11-12/group). Bar graphs represent mean ± SEM after combining male and female data.