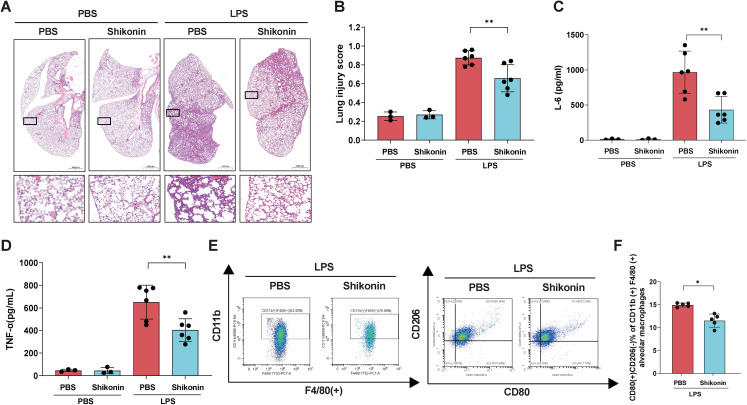
Figure 4.
The PKM2 inhibitor shikonin alleviated the LPS-induced macrophage inflammation and lung injury. Notes: (A–F) Male C57BL/6 mice were administered shikonin (8 mg/kg) or PBS intraperitoneally every 8 h with a single dose of LPS (5 mg/kg) or PBS at 6 h after the first treatment (n = 6 per group). (A) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of lung tissues of the four groups was assessed 24 h after LPS injection. (B) Lung injury score assessment (n = 6, LPS injected group; and n = 3, control group). (C-D) The levels of IL-6 and TNF-α in BALF 24 h after LPS injection, as assessed via ELISA (n = 6, LPS injected group; and n = 3, control group). (E) CD80 (+) CD206 (-) cells of F4/80 (+) cells from BALF. (F) Percentage of CD80 (+) CD206 (-) cells out of all CD11b (+) F4/80 (+) cells. The graphs show the means ± SDs, and the data shown in A–F are representative of three independent experiments. Values of p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant, and data marked with a one (*), two (**) and three (***) asterisks indicate p values of <0.05, < 0.01 and <0.001, respectively. LPS, lipopolysaccharide; IL, interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; PKM2, pyruvate kinase M2.