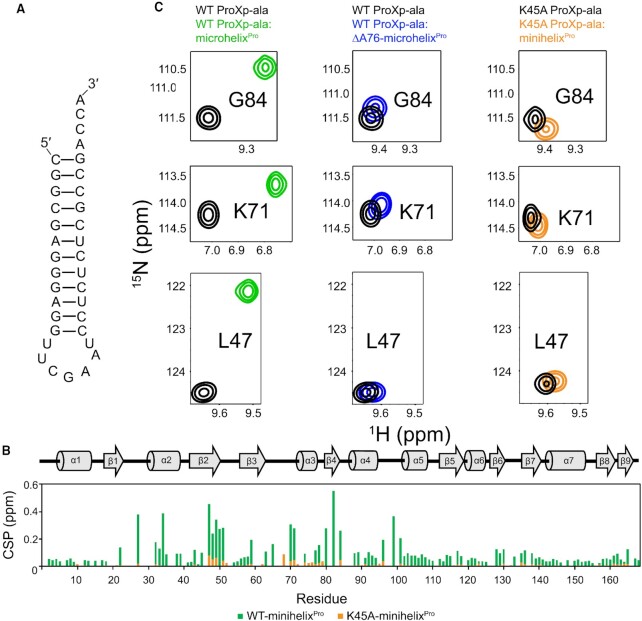
Figure 6.
CSPs show parallel ProXp-ala-tRNAPro binding deficiencies upon deletion of A76 and mutation of K45. (A) Schematic of minihelixPro, which is indistinguishable from microhelixPro in terms of its binding to ProXp-ala (Supplementary Fig. 4). (B) Secondary structure of Cc ProXp-ala (top) and summary of per residue CSPs induced by minihelixPro binding to WT (green) and K45A (orange) ProXp-ala. (C) Spectral expansions of Gly84 (top), Lys71 (middle) and Leu47 (bottom) from overlaid 1H–15N HSQC spectra of WT ProXp-ala (left and middle spectra) free (black), and in the presence of microhelixPro (green) or ΔA76-microhelixPro (blue), and of K45A ProXp-ala (right spectra) free (black), and in the presence of minihelixPro-bound (orange).