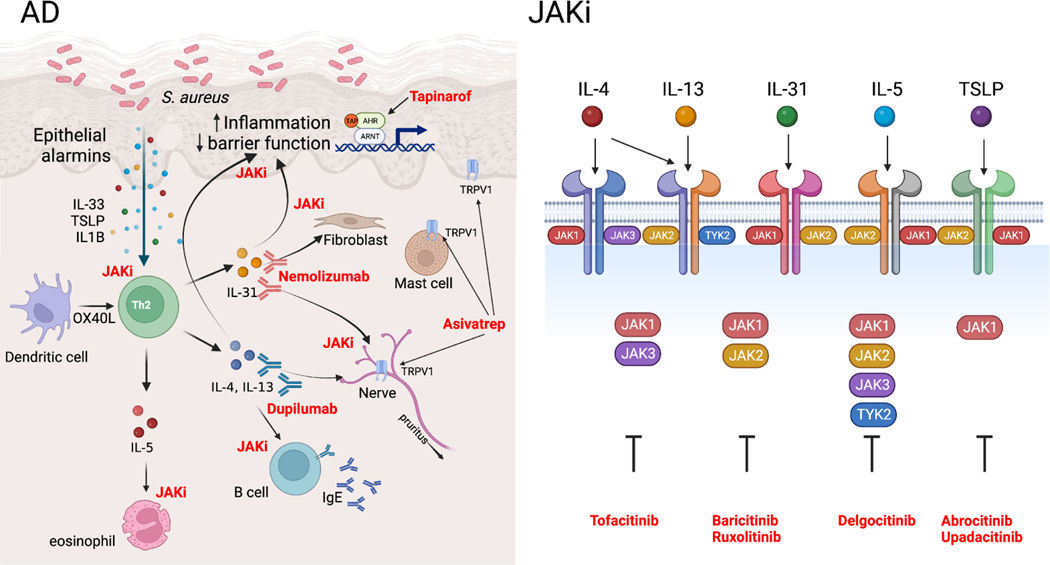
Figure 2. Novel therapeutic advances in AD.
Left panel, Intersection between therapeutic development and atopic dermatitis (AD) pathogenesis with therapeutic agents shown in red next to their biologic mechanisms of action. Right panel, Janus kinase (JAK) family members dimerize to mediate different cytokine responses. JAK inhibitors (JAKi) inhibit multiple aspects of AD pathogenesis through targeting of select JAK family members (right panel modified from Chovatiya et. al. (93)).