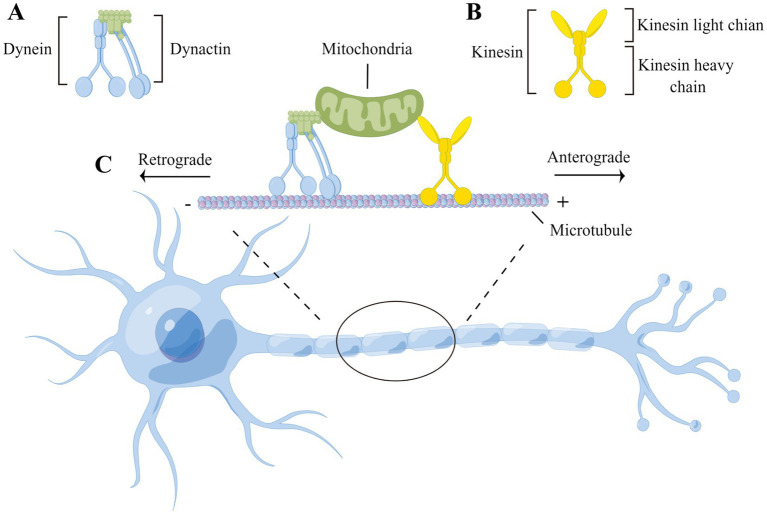
Figure 1.
Microtubule-based neuronal axonal transport. (A) Dynein transport complex consists of dynein’s heavy, medium, medium-light, and light chains and dynactin, which move along the axon to transport cargoes in a retrograde direction (i.e., toward the minus end of the microtubule and cell body); (B) Kinesin consists of two heavy chains and two light chains, which transport cargoes in a anterograde direction along the axon (i.e., toward the plus end of the microtubule and synaptic terminals); (C) The heavy chains of both kinesin and dynein have a motor structural domain that binds to the microtubule, hydrolyzes ATP, and propels cargo along the microtubule track. The cargoes are attached to motor proteins via kinesin’s light chain or dynactin.