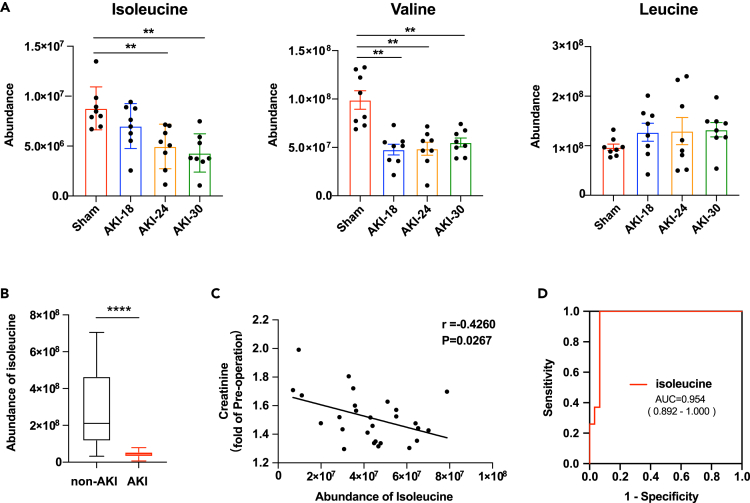
Figure 5.
Reduction of neutral amino acid isoleucine in plasma of AKI mouse and human with CSA-AKI
(A) Boxplots showing the abundance of isoleucine, valine and leucine in plasma of sham or AKI mice. n = 8 for each group. ∗∗p < 0.01, compared to Sham group, One-way ANOVA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
(B) Boxplots showing the concentration of isoleucine in plasma of patients with or without CSA-AKI. n = 30 for non-AKI group, n = 27 for AKI group. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, Student’s t test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
(C) The correlation analysis between the abundance of isoleucine and the serum creatinine (fold of pre-operation) of patients with CSA-AKI. n = 27, Pearson correlation analysis.
(D) ROC curve for diagnostic value of isoleucine to differentiate patients with AKI from patients without AKI after cardiac surgery. CSA-AKI indicates cardiac surgery–associated AKI; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; AUC, area under the curve.