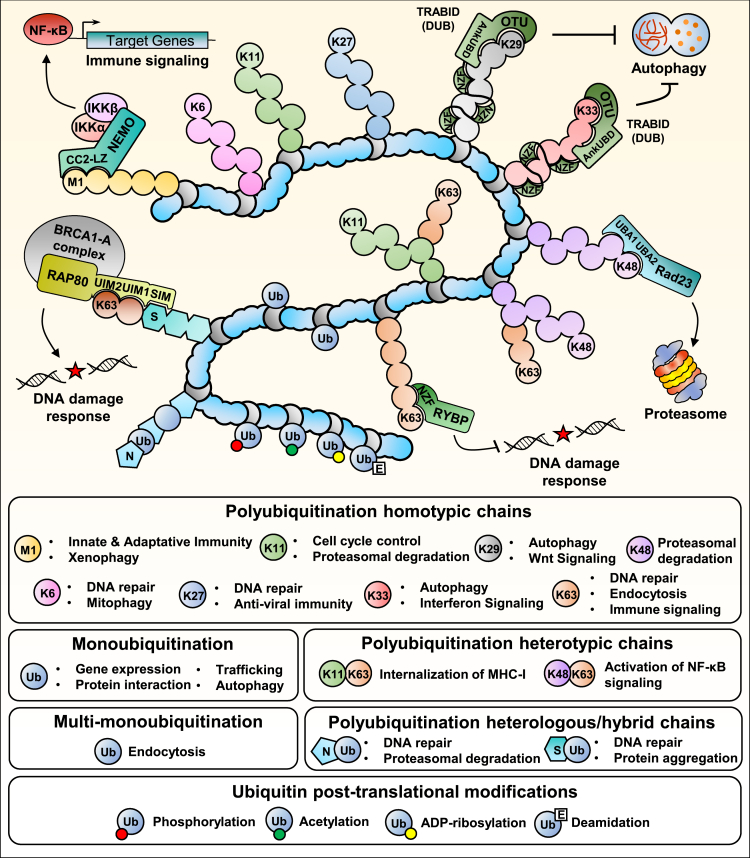
Figure 2.
Ubiquitin chains and their functions
Ubiquitination of proteins is catalyzed by the action of E1 ubiquitin-activating, E2 ubiquitin-conjugating, and E3 ubiquitin-ligating enzymes. The concerted action of E2 and E3 enzymes dictates the nature of ubiquitin modification. Ubiquitination is reversed by deubiquitinases (DUBs). A protein target (in blue) can be monoubiquitinated, multi-monoubiquitinated, or polyubiquitinated. Monoubiquitination and multi-monoubiquitination are associated with diverse signaling pathways and processes including intracellular membrane trafficking, transcription regulation, DNA damage signaling and repair as well as the regulation of protein subcellular localization. Monoubiquitination events have also been shown to induce proteasomal degradation. Polyubiquitination involves eight ubiquitin linkage types, i.e., M1, K6, K11, K27, K29, K33, K48, and K63. The various ubiquitin chains are associated with numerous functional and biological outcomes. K63 polyubiquitin chains are associated with protein recruitment and activation of signaling cascades, K48 polyubiquitin chains generally promote the proteasomal degradation of substrates. Polyubiquitination can generate homotypic, heterotypic, or heterologous chains that add another layer of complexity to ubiquitin signaling pathways. Moreover, post-translational modifications of ubiquitin itself (phosphorylation, acetylation, ADP-ribosylation, and deamidation) can modulate E3 ligase activity and interfere with ubiquitin ligation or ubiquitin chain elongation. Following substrate ubiquitination, ubiquitin chains could be recognized by a wide variety of ubiquitin-binding proteins through their ubiquitin-binding domains (UBD). Examples of UBDs are represented by the ubiquitin interacting motifs (UIM) of RAP80, the Ubiquitin-associated domains (UBA) of Rad23, or the Npl4-like Zinc Finger (NZF) of the deubiquitinase TRABID. A wide range of signaling events and biological processes are associated with ubiquitin binding such as the DNA damage response, cell death, immune signaling, and autophagy.