Fig. 2.
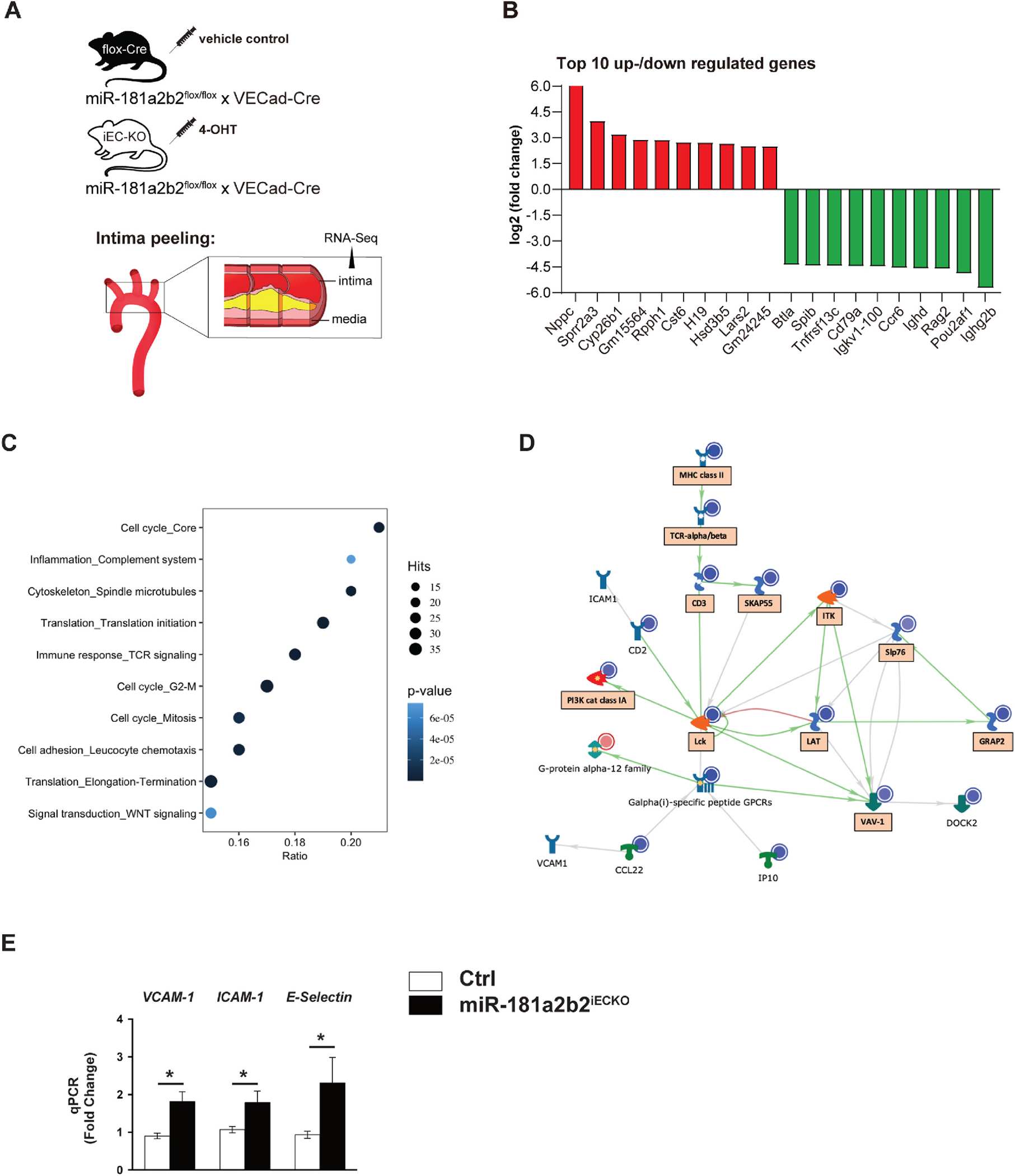
Lesional RNA-Seq studies from miR-181a2b2iECKO mice reveal activation of pathways involved in cell adhesion, cell cycle, and immune response.
(A) Scheme of experimental procedure. RNA sequence analysis of RNA isolated from aortic arch intimal ECs miR-181a2b2 sufficient (Ctrl) or 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT)-induced endothelial cell (EC)-specific miR-181a2b2 deficient (miR-181a2b2ECKO) mice after 12 weeks of high cholesterol diet and AAV-PCSK9D377Y injection as described in Fig. 1. (B) Top 10 up- or downregulated genes by fold change. (C) Gene set enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes. Hits represent the number of differentially expressed genes per network. Color denotes p-value. Ratio represents the number of regulated genes divided by the number of expected genes from each network. (D) The network of regulated gene interactions within the ‘cell adhesion’ pathway. The objects that are up- or downregulated are marked with red or blue circles, respectively. Arrow color represents activation (green), inhibition (red), or unspecified (grey) effects. Genes in boxes are also found in ‘immune response’ and ‘inflammation’ pathways. (E) qPCR analysis of the indicated proinflammatory genes in the endothelial enriched intima from aortic arch. The expression of inflammatory genes was normalized to mouse β-actin expression. Data shown are mean ± SEM. (B to D), n = 3 mice per group. (E) n = 4 mice per group. *p < 0.05, N.S. indicates nonsignificance.
