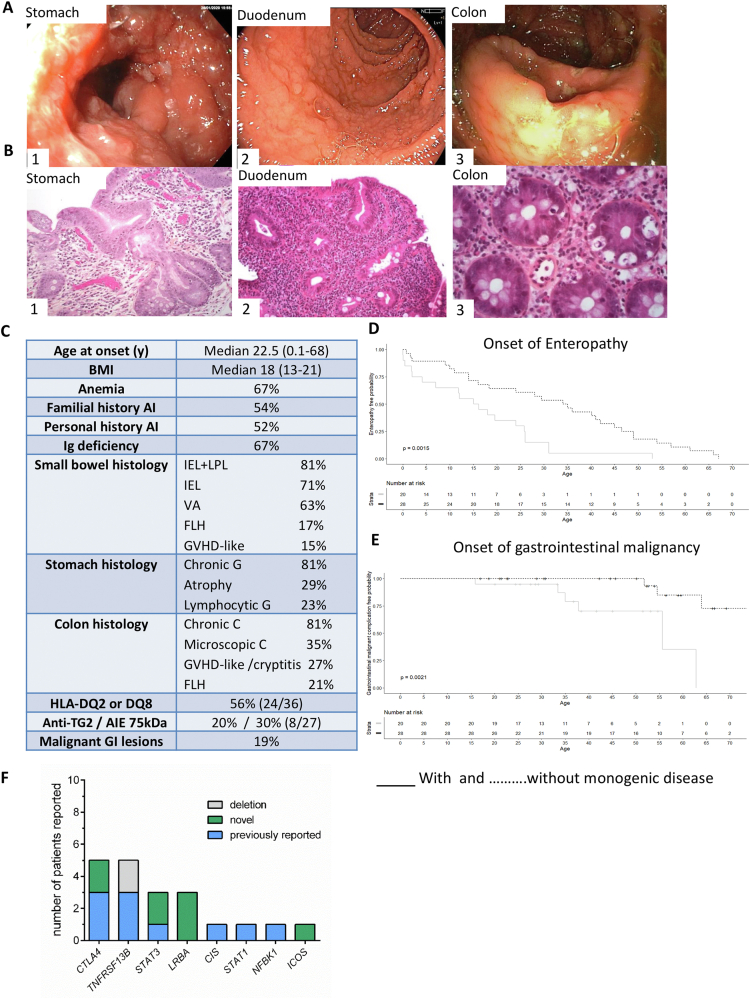
Figure 1.
(A) Representative endoscopic aspects in patients with CTLA4 variants and AIE. (1) Ulcerative gastritis with pseudobstruction in patient P9. (2) Duodenal villous atrophy in P1. (3) Colitis with ulcerations in P9. (B) Representative histologic lesions in patients with AIE. (1) Chronic fundic atrophic gastritis with intestinal metaplasia and focal low-grade dysplasia (×200) in P9 carrying a CTLA4 variant. (2) Chronic duodenitis in P1 with CTLA4 mutation with severe villous blunting and increased IEL numbers (×200). (3) Colitis with GVHD-like lesions and cryptic apoptotic bodies (×400) in a patient without identified pathogenic variant (description of numbered patients is provided in Supplementary Table 1). (C) Clinical features of the 48 patients with AIE. (D) Kaplan-Meier enteropathy-free survival curve of patients with (solid line) or without molecular diagnosis (dashed line). (E) Kaplan-Meier gastrointestinal malignant-free survival curve of patients with (solid line) or without molecular diagnosis (dashed line). (F) Number of patients for each individual molecular diagnosis. anti-TG2, antitransglutaminase of type 2; AI, autoimmune; AIE-75kDa, autoimmune enteropathy-related 75-kilodalton antibody; BMI, body mass index; C, colitis; IEL, intestinal intraepithelial hyperlymphocytosis; FLH, follicular lymphoid hyperplasia; G, gastritis; GI, gastrointestinal; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; LPL, lamina propria hyperlymphocytosis; VA, villous atrophy.