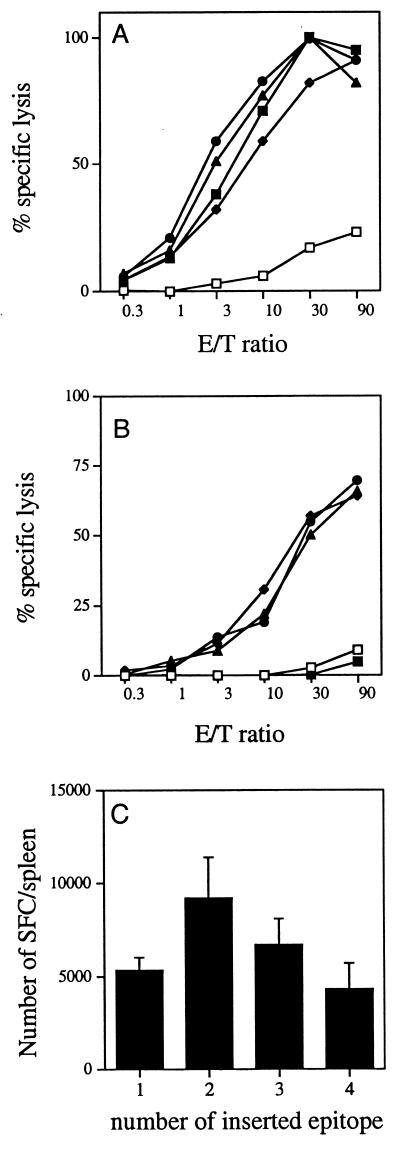
FIG. 4.
Induction of LCMV-specific CTL responses by CyaA carrying one, two, three, or four copies of the LCMV epitope. (A and B) On days 0 and 21, BALB/c mice were injected i.p. with control wild-type CyaA (□) or recombinant toxin CyaA224LCMV1 (⧫), CyaA224LCMV2 (●), CyaA224LCMV3 (▴), or CyaA224LCMV4 (■). Seven days after the last injection, spleen cells were stimulated in vitro with the LCMV peptide and then tested for CTL activity on 51Cr-labeled P815 target cells incubated with the same peptide. No specific lysis was obtained on P815 target cells incubated with medium alone. (A) Mice injected twice with 10 μg of toxin in the presence of 1 mg of alum; (B) mice injected twice with 10 μg of toxin without adjuvant. Standard deviations were always <10% of the maximum response. (C) Quantitation of the LCMV-specific T-cell responses. BALB/c mice were immunized i.p. on days 0 and 21 with 50 μg of CyaA-wt or CyaA224LCMV1, CyaA224LCMV2, CyaA224LCMV3, CyaA224LCMV4 toxins (bars 1 through 4, respectively) in the presence of 1 mg of alum. Seven days after the last injection, the frequency of LCMV-specific T cells in the spleen was measured by the single-cell IFN-γ ELISPOT assay in the presence of p118-132 as described in Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as the number of SFC per spleen and represent the mean for four mice in each group plus standard deviation. No SFC were obtained in the absence of p118-132 or with spleen cells from mice immunized with CyaA-wt and stimulated in the presence of p118-132.