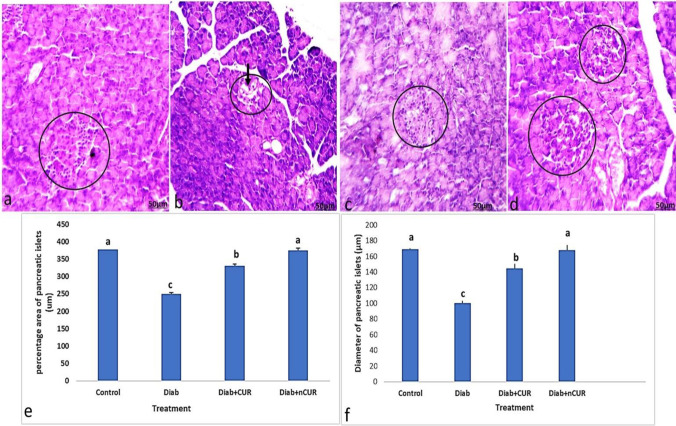
Fig. 3.
a–d Photomicrographs of sections of the pancreas stained by H&E. a Section from control group showed normal alpha-cells and beta cells (circle). b Section from pancreas of Diab rat showed atrophy and cytoplasmic degenerative changes (arrow) in most islet cells, especially in center of the islet (circle). c Section from pancreas of (Diab + CUR) STZ-induced diabetic rats that were given a daily oral dose of 100 mg/kg/day of curcumin showed very similar morphology to the control group. d Section from rat of (Diab + nCUR) STZ-induced diabetic rats that were given a daily oral dose of 100 mg/kg/day of nano-curcumin showed nearly regular outline of an islet with apparently normal appearance of most cells (H&E staining, × 100). e, f Histomorphometric measurements showed changes in the mean values of the following: e percentage area of pancreatic islets cells (%); f diameter of islet cells. Data was expressed as mean ± SE. Statistical significance was evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test at P < 0.05. The mean values with different superscript letters on the bars were significantly different at P < 0.05. Diab, STZ-induced diabetic rats; Diab + CUR, STZ-induced diabetic rats that were given a daily oral dose of 100 mg/kg/day of curcumin were dissolved in carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) 1:10 (w/v); Diab + nCUR, STZ-induced diabetic rats that were given a daily oral dose of 100 mg/kg/day of nano-curcumin were dissolved in CMC 1:10 (w/v)