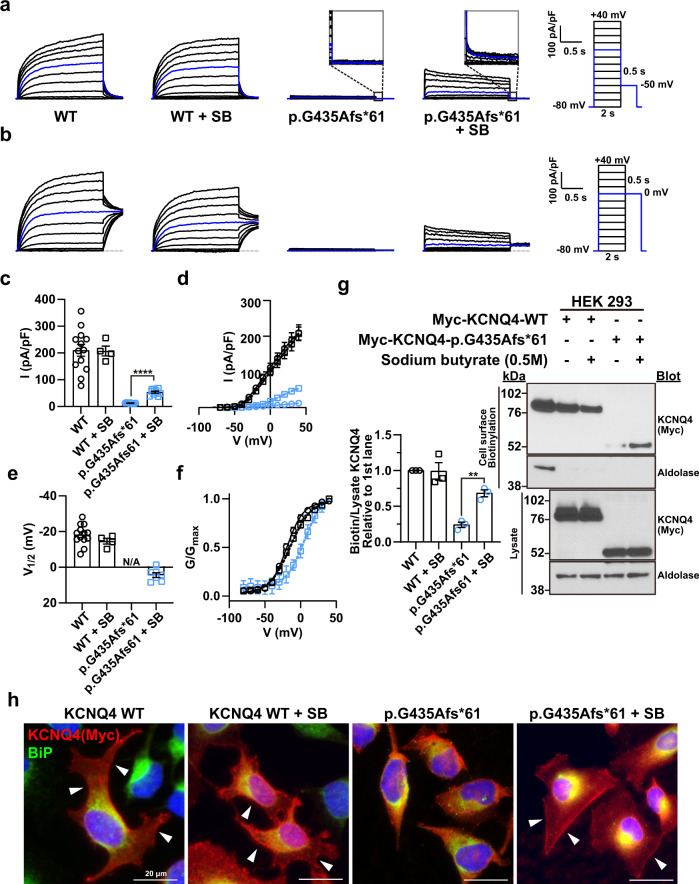
Fig. 5. Effect of sodium butyrate on the p.G435Afs*61 variant.
a, b Whole-cell currents recorded from HEK 293 cells overexpressing WT KCNQ4 or p.G435Afs*61 variant proteins treated with 0.5 M sodium butyrate (SB) for 18 h. From a holding potential of −80 mV, currents were evoked by depolarizing voltage steps from −80 to 40 mV in 10 mV increments. The tail currents were set to −50 mV in (a) and 0 mV in (b) after each voltage step. The blue line indicates the current measured at a 0 mV test pulse. c Current density measured at 40 mV. d Mean current-voltage (I-V) relationship. Trace representatives are the same as in (c). e Half-maximal voltages calculated by fitting the normalized conductance to the Boltzmann equation. f Normalized conductance-voltage (G/Gmax-V) relationship. The curves were fitted using the Boltzmann equation. Trace representatives are the same as (e). g Immunoblotting with surface biotinylation assay of WT and p.G435Afs*61 variant treated with 0.5 M sodium butyrate (SB) for 18 h. h Immunofluorescence of WT and p.G435Afs*61 variant treated with 0.5 M SB in HeLa cells. Arrows indicate the membrane expression of KCNQ4 WT and p.G435Afs*61 proteins. Values are shown as the mean ± SEM. p values were calculated using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test; p < 0.01, **p < 0.0001, ****.