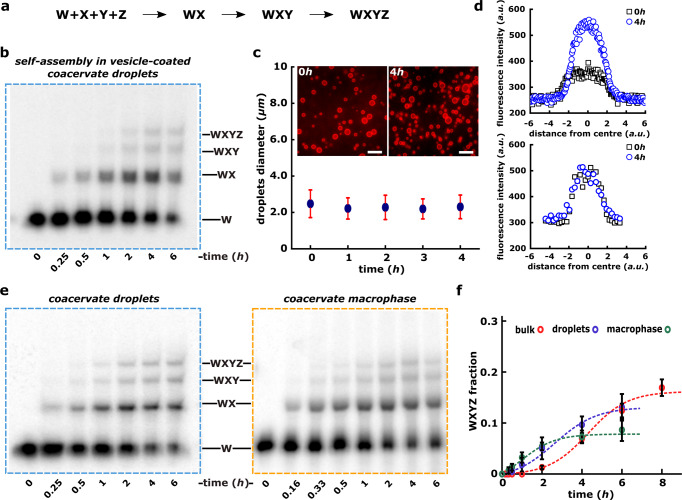
Fig. 2. Autocatalytic self-assembly of the Azoarcus ribozyme in coacervates.
a Schematic showing the systematic assembly of covalent ribozyme (WXYZ) from smaller inactive RNA fragments W, X, Y, Z via WX, WXY intermediates. b Polyacrylamide gel showing the self-assembly of Azoarcus ribozyme (WXYZ) from its small RNA fragments (W, X, Y, Z) inside the vesicle-coated coacervate droplets demonstrating that WXYZ formation indeed occurs inside the micron-size droplets. Here coacervate droplets were prepared together with RNA fragments (W, X, Y, and Z) and then coated with lipid vesicles (DOPC) prior to incubating at 48 °C and analyzed over polyacrylamide gel (see “Methods”). c Graph showing the stability of vesicle-coated coacervates during the reaction time course shown in b. Here average droplet diameter is plotted over the time. The microscopy images of vesicle-coated coacervate droplets (at 0 h and 4 h) are shown in inset. The fluorescence is due to the doping of 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-(lissamine rhodamine B sulfonyl) with the DOPC lipid (see “Methods”). d Graph showing the leakiness of the vesicle-coated coacervate used for the self-assembly reaction shown in b. The leakiness is tested as increase in fluorescence intensity of the coacervate droplets due to the diffusion of a 30-nt Alexa-488 DNA oligonucleotide (same as used in FRAP studies above, Fig. 1) from bulk solution to the vesicle-coacervate droplets. Leakiness is measured either for the 30-nt Alexa-488 DNA oligonucleotide alone (top) or hybridized to the ~200-nt Azoarcus ribozyme (bottom). Here the fluorescence intensity is plotted against distance from the center of the droplet. See “Methods” for the details. e Polyacrylamide gels showing the time course for the formation of full-length product (covalent ribozyme, WXYZ) starting from smaller RNA fragments inside coacervate droplets (left) as well as inside coacervate macrophase (right). The reaction samples are doped with (γ32P) labeled W RNA fragment (0.01 μM) added and folded together with all the fragments (W, X, Y, and Z, 0.75 μM each). See “Methods” for the experimental details. After incubation, samples are processed and analyzed via 12% denaturing PAGE. f Time courses showing the autocatalytic self-assembly of WXYZ ribozyme from W, X, Y, and Z RNA fragments in coacervate macrophase (green circles), coacervate droplets (blue circles) and as well as in bulk aqueous phase control (red circles). Reactions are done by encapsulating the substrate fragments in coacervates, separating the macrophase, or by incubating the droplets directly at 48 °C (Supplementary Fig. S2 and “Methods”). All the time courses are measured in triplicates and mean WXYZ product formation is plotted along with standard deviation. The time-course data is also analyzed by a kinetic model described for the Azoarcus assembly earlier36 and the fitted curves are shown as dotted lines (green, blue, and red for the macrophase, droplets, and bulk aqueous phase, respectively).